目录
- 使用范例
- 常用的对象–Tag
- 常用的对象–NavigableString
- 常用的对象–BeautifulSoup
- 常用的对象–Comment
- 对文档树的遍历
- tag中包含多个字符串的情况
- .stripped_strings 去除空白内容
- 搜索文档树–find和find_all
- select方法(各种查找)
- 获取内容
- 总结
使用范例
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
#创建 Beautiful Soup 对象
# 使用lxml来进行解析
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,"lxml")
print(soup.prettify())
返回结果
常用的对象–Tag
就是 HTML 中的一个个标签
在上面范例的基础上添加
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
#创建 Beautiful Soup 对象
# 使用lxml来进行解析
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,"lxml")
#print(soup.prettify())
#创建 Beautiful Soup 对象
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print (soup.title)#None因为这里没有tiele标签所以返回none
print (soup.head)#None因为这里没有head标签所以返回none
print (soup.a)#返回 a class="fill-dec" href="//my.csdn.net" target="_blank">编辑自我介绍,让更多人了解你span class="write-icon">/span>/a>
print (type(soup.p))#返回 class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
print( soup.p)
其中print( soup.p)
返回结果为
同样地,在上面地基础上添加
print (soup.name)# [document] #soup 对象本身比较特殊,它的 name 即为 [document]
返回

print (soup.head.name)#head #对于其他内部标签,输出的值为标签本身的名称
print (soup.p.attrs)##把p标签的所有属性打印出来,得到的类型是一个字典。
返回

print (soup.p['class'])#获取P标签下地class标签
soup.p['class'] = "newClass"
print (soup.p) # 可以对这些属性和内容等等进行修改
返回
常用的对象–NavigableString
前面地基础上添加
print (soup.p.string)
# The Dormouse's story
print (type(soup.p.string))
# class 'bs4.element.NavigableString'>thon
返回结果

常用的对象–BeautifulSoup
beautiful soup对象表示文档的全部内容。大多数情况下,它可以被视为标记对象。它支持遍历文档树并搜索文档树中描述的大多数方法因为Beauty soup对象不是真正的HTML或XML标记,所以它没有名称和属性。但是,有时查看其内容很方便。Name属性,因此美丽的汤对象包含一个特殊属性。值为“[文档]”的名称
print(soup.name)
#返回 '[document]'
常用的对象–Comment
用于解释注释部分的内容
markup = "b>!--Hey, buddy. Want to buy a used parser?-->/b>"
soup = BeautifulSoup(markup)
comment = soup.b.string
type(comment)
# class 'bs4.element.Comment'>
对文档树的遍历
在上面的基础上添加
head_tag = soup.div
# 返回所有子节点的列表
print(head_tag.contents)
返回
同理
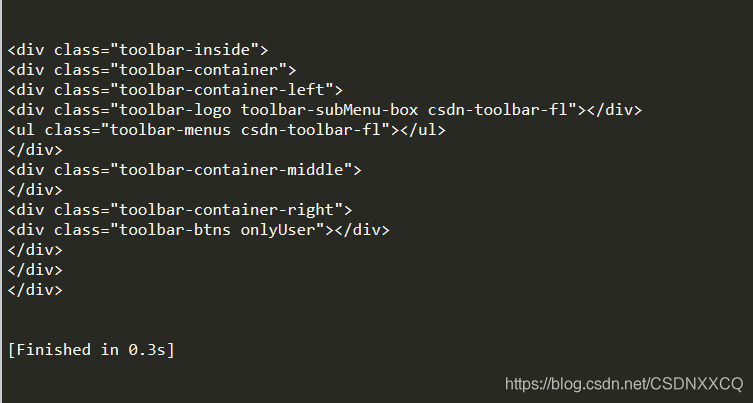
head_tag = soup.div
# 返回所有子节点的迭代器
for child in head_tag.children:
print(child)
返回
tag中包含多个字符串的情况
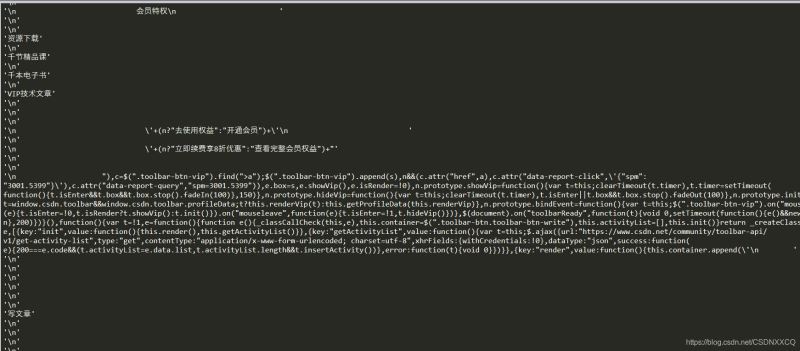
可用 .strings 来循环获取
for string in soup.strings:
print(repr(string))
返回
.stripped_strings 去除空白内容
for string in soup.stripped_strings:
print(repr(string))
返回

搜索文档树–find和find_all
找到所有
print(soup.find_all("a",id='link2'))
find方法是找到第一个满足条件的标签后立即返回,返回一个元素。find_all方法是把所有满足条件的标签都选到,然后返回。
select方法(各种查找)
#通过标签名查找:
print(soup.select('a'))
#通过类名查找:
#通过类名,则应该在类的前面加一个'.'
print(soup.select('.sister'))
#通过id查找:
#通过id查找,应该在id的名字前面加一个#号
print(soup.select("#link1"))
查找a标签返回的结果
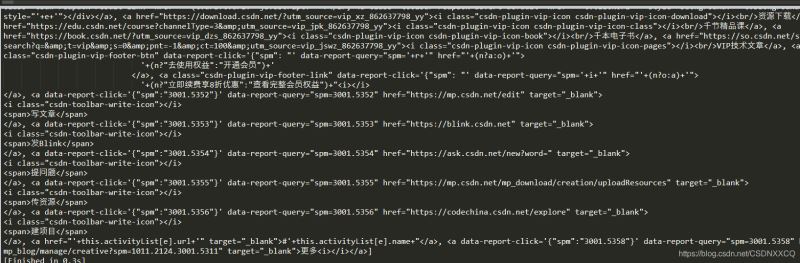
其他因为网页本身没有,返回的是一个空列表
组合查找
print(soup.select("p #link1"))#查找 p 标签中,id 等于 link1的内容
子标签查找
print(soup.select("head > title"))
通过属性查找
print(soup.select('a[href="http://example.com/elsie"]'))#属性与标签属同一节点,中间不能有空格
获取内容
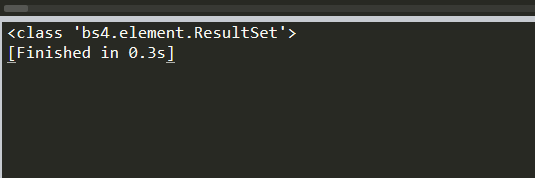
先查看类型
print (type(soup.select('div')))
for title in soup.select('div'):
print (title.get_text())
返回

print (soup.select('div')[20].get_text())#选取第20个div标签的内容
返回
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注脚本之家的更多内容!
您可能感兴趣的文章:- Python BeautifulSoup基本用法详解(通过标签及class定位元素)
- python beautiful soup库入门安装教程
- Python爬虫进阶之Beautiful Soup库详解
- python爬虫beautifulsoup库使用操作教程全解(python爬虫基础入门)
- python网络爬虫精解之Beautiful Soup的使用说明
 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服