目录
- arrow模块的使用
- 获取当前时间
- 时间形式转换
- 转换成时间字符串
- 转换成时间戳
- 获取数据
- 修改时间
- 将字符串转换为arrow对象 arrow.get(string[,format_string])
- 获取datetime对象的值
- 时间推移 a.shift(**kwargs)
- 时间替换 a.replace(**kwargs)
- 格式化输出 a.format([format_string])
- 最牛的是这个人性化输出 a.humanize()
Python中有很多时间和日期处理的库,有time、datetime等,虽然提供了很完整的对日期、时间以及时区转换处理的功能,但是方法过多,不易于记忆,而且经常需要各种转换操作,非常繁琐,比如时间和时间戳的转换,格式化时间字符串转换等等,几乎每次使用都要先看一下教程文档。那么有没有使用起来更人性化的日期时间处理库呢?接下来就来看一下arrow日期时间库。
arrow是一个专门处理时间和日期的轻量级Python库,它提供了一种合理、人性化的方式来创建、操作、格式化、转换日期、时间和时间戳,可以比较轻易的创建具有时区意识的日期和时间实例。
可以使用pip install arrow进行安装。
arrow模块的使用
获取arrow对象
Arrow可以很灵活的将多种格式的时间数据转换成Arrow对象,如下:
import arrow
print(repr(arrow.Arrow(2021, 8, 23, 8)))
print(repr(arrow.get(2021, 8, 23, 8, 40)))
print(repr(arrow.get('2021-08-23 09:00')))
print(repr(arrow.get('2021.08.23')))
print(repr(arrow.get('23/2012/08', 'DD/YYYY/MM')))
执行结果如下:
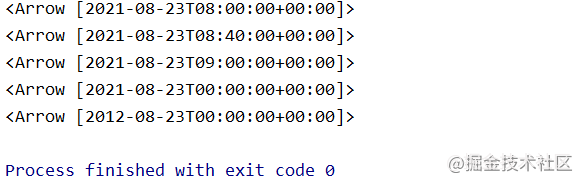
上面几种方式都可以将字符数据转换为arrow对象,转换非常灵活。除此之外,还可以把时间戳转换为arrow对象。
print(repr(arrow.get(1629683393.6558669)))
获取当前时间
utc_time = arrow.utcnow()
local_time = arrow.now()
print(utc_time)
print(local_time)
通过utcnow()函数和now()函数分别获取的是utc时间和本地时间,当然我们也可以在调用now()时指定时区,从而获取指定时区的时间,例如arrow.now('US/Pacific')。
时间形式转换
使用日期时间的时候我们经常需要转换操作,比如转换成指定格式的时间字符串,转换成时间戳等。
转换成时间字符串
now = arrow.now()
print(now)
print(now.format())
print(now.format("YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss"))
print(now.format("YYYY-MM-DD"))
执行结果如下:

看到这个,是不是感觉比datetime模块的'%Y-%M-%D %h:%m:%s'格式化方式更人性化更便于记忆呢。
转换成时间戳
可以使用t.timestamp将arrow对象转换成时间戳。
获取数据
转换为Arrow对象后,我们可以很方便的获取我们想要的各种时间数据,通过year、month、day、hour、minute、second、week等属性,如:
now = arrow.now()
print(now.year)
print(now.month)
print(now.day)
print(now.hour)
print(now.minute)
print(now.second)
print(now.week)
修改时间
有时拿到一个时间时,我们需要对时间就行修改,例如修改时区、修改时间等等,我们可以使用以下方式去修改。
now = arrow.now()
print(now.format("YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss")) # 2021-08-23 10:11:04
now_utc = now.to("utc")
print(now_utc.format("YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss")) # 2021-08-23 02:11:04
now1 = now.replace(day=31, hour=12)
print(now1.format("YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss")) # 2021-08-31 12:11:04
now2 = now.shift(months=-2)
print(now2.format("YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss")) # 2021-06-23 10:11:04
我们可以使用to()方法切换时区,使用replace()方法修改时间,使用shift()进行时间的前后推移。
将字符串转换为arrow对象 arrow.get(string[,format_string])
In [52]: arrow.get('2018-03-22 23:35:34')
Out[52]: Arrow [2018-03-22T23:35:34+00:00]>
可以从字符串中通过格式参数搜索时间
In [13]: arrow.get('june waw born in May 1999', 'MMMM YYYY')
Out[13]: Arrow [1999-05-01T00:00:00+00:00]>
arrow对象属性 datetime,timestamp,naive,tzinfo
In [54]: t.datetime
Out[54]: datetime.datetime(2019, 3, 22, 21, 39, 0, 223147, tzinfo=tzlocal())
In [55]: t.timestamp
Out[55]: 1553261940
In [58]: t.tzinfo
Out[58]: tzlocal()
In [59]: t.naive
Out[59]: datetime.datetime(2019, 3, 22, 21, 39, 0, 223147)
获取datetime对象的值
In [60]: t.year
Out[60]: 2019
In [62]: t.month
Out[62]: 3
In [63]: t.day
Out[63]: 22
In [64]: t.hour
Out[64]: 21
时间推移 a.shift(**kwargs)
shift方法获取某个时间之前或之后的时间,关键字参数为years,months,weeks,days,hours,seconds,microseconds
In [65]: t.shift(weeks=-1)
Out[65]: Arrow [2019-03-15T21:39:00.223147+08:00]>
In [66]: t.shift(days=20)
Out[66]: Arrow [2019-04-11T21:39:00.223147+08:00]>
In [67]: t.shift(hours=1)
Out[67]: Arrow [2019-03-22T22:39:00.223147+08:00]>
时间替换 a.replace(**kwargs)
返回一个被替换后的arrow对象,原对象不变
In [68]: t.replace(year=2018)
Out[68]: Arrow [2018-03-22T21:39:00.223147+08:00]>
In [69]: t
Out[69]: Arrow [2019-03-22T21:39:00.223147+08:00]>
格式化输出 a.format([format_string])
In [70]: t.format()
Out[70]: '2019-03-22 21:39:00+08:00'
In [71]: t.format('YYYY-MM-DD HH-MM-SS')
Out[71]: '2019-03-22 21-03-22'
最牛的是这个人性化输出 a.humanize()
In [72]: t.humanize()
Out[72]: '2 hours ago
同Python内置日期datetime库一样,arrow对象也支持时间的大小对比,还有计算时间差操作,除此之外,还有很多意想不到的操作,感兴趣的话,可以查看官方文档:Arrow: Better dates times for Python — Arrow 🏹 1.1.1 documentation)
到此这篇关于Python日期时间模块arrow的具体使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python日期时间模块arrow 内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
您可能感兴趣的文章:- Python 处理日期时间的Arrow库使用
- 关于Python 中的时间处理包datetime和arrow的方法详解
- Python使用arrow库优雅地处理时间数据详解
 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服