目录
- 概述
- 会用到的函数
- 张量最小值
- 张量最大值
- 数据集分批
- 迭代
- 截断正态分布
- relu 激活函数
- one_hot
- assign_sub
- 准备工作
- run 函数
- 完整代码
概述
前向传播 (Forward propagation) 是将上一层输出作为下一层的输入, 并计算下一层的输出, 一直到运算到输出层为止.
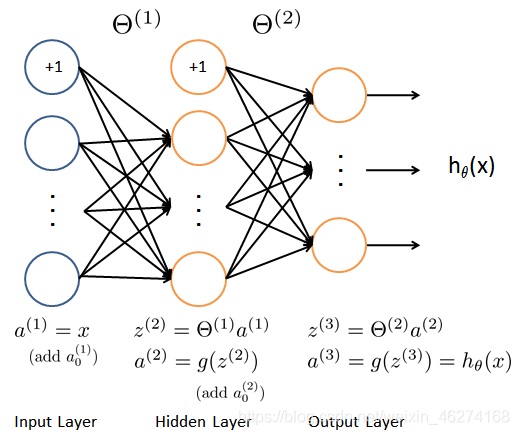
会用到的函数

张量最小值
```reduce_min``函数可以帮助我们计算一个张量各个维度上元素的最小值.
格式:
tf.math.reduce_min(
input_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=False, name=None
)
参数:
- input_tensor: 传入的张量
- axis: 维度, 默认计算所有维度
- keepdims: 如果为真保留维度, 默认为 False
- name: 数据名称
张量最大值
```reduce_max``函数可以帮助我们计算一个张量各个维度上元素的最大值.
格式:
tf.math.reduce_max(
input_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=False, name=None
)
参数:
- input_tensor: 传入的张量
- axis: 维度, 默认计算所有维度
- keepdims: 如果为真保留维度, 默认为 False
- name: 数据名称
数据集分批
from_tensor_slices可以帮助我们切分传入 Tensor 的第一个维度. 得到的每个切片都是一个样本数据.

格式:
@staticmethod
from_tensor_slices(
tensors
)
迭代
我们可以调用iter函数来生成迭代器.
格式:
参数:
-object: 支持迭代的集合对象
- sentinel: 如果传递了第二个参数, 则参数 object 必须是一个可调用的对象 (如, 函数). 此时, iter 创建了一个迭代器对象, 每次调用这个迭代器对象的
__next__()方法时, 都会调用 object
例子:
list = [1, 2, 3]
i = iter(list)
print(next(i))
print(next(i))
print(next(i))
输出结果:
1
2
3
截断正态分布
truncated_normal可以帮助我们生成一个截断的正态分布. 生成的正态分布值会在两倍的标准差的范围之内.
格式:
tf.random.truncated_normal(
shape, mean=0.0, stddev=1.0, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32, seed=None, name=None
)
参数:
- shape: 张量的形状
- mean: 正态分布的均值, 默认 0.0
- stddev: 正态分布的标准差, 默认为 1.0
- dtype: 数据类型, 默认为 float32
- seed: 随机数种子
- name: 数据名称
relu 激活函数
激活函数有 sigmoid, maxout, relu 等等函数. 通过激活函数我们可以使得各个层之间达成非线性关系.
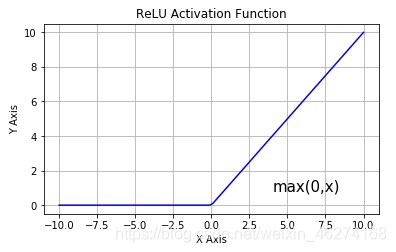
激活函数可以帮助我们提高模型健壮性, 提高非线性表达能力, 缓解梯度消失问题.
one_hot
tf.one_hot函数是讲 input 准换为 one_hot 类型数据输出. 相当于将多个数值联合放在一起作为多个相同类型的向量.
格式:
tf.one_hot(
indices, depth, on_value=None, off_value=None, axis=None, dtype=None, name=None
)
参数:
- indices: 索引的张量
- depth: 指定独热编码维度的标量
- on_value: 索引 indices[j] = i 位置处填充的标量,默认为 1
- off_value: 索引 indices[j] != i 所有位置处填充的标量, 默认为 0
- axis: 填充的轴, 默认为 -1 (最里面的新轴)
- dtype: 输出张量的数据格式
- name:数据名称
assign_sub
assign_sub可以帮助我们实现张量自减.
格式:
tf.compat.v1.assign_sub(
ref, value, use_locking=None, name=None
)
参数:
- ref: 多重张量
- value: 张量
- use_locking: 锁
- name: 数据名称
准备工作

import tensorflow as tf
# 定义超参数
batch_size = 256 # 一次训练的样本数目
learning_rate = 0.001 # 学习率
iteration_num = 20 # 迭代次数
# 读取mnist数据集
(x, y), _ = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data() # 读取训练集的特征值和目标值
print(x[:5]) # 调试输出前5个图
print(y[:5]) # 调试输出前5个目标值数字
print(x.shape) # (60000, 28, 28) 单通道
print(y.shape) # (60000,)
# 转换成常量tensor
x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255 # 转换为0~1的形式
y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y, dtype=tf.int32) # 转换为整数形式
# 调试输出范围
print(tf.reduce_min(x), tf.reduce_max(x)) # 0~1
print(tf.reduce_min(y), tf.reduce_max(y)) # 0~9
# 分割数据集
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x, y)).batch(batch_size) # 256为一个batch
train_iter = iter(train_db) # 生成迭代对象
# 定义权重和bias [256, 784] => [256, 256] => [256, 128] => [128, 10]
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([784, 256], stddev=0.1)) # 标准差为0.1的截断正态分布
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256])) # 初始化为0
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([256, 128], stddev=0.1)) # 标准差为0.1的截断正态分布
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([128])) # 初始化为0
w3 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([128, 10], stddev=0.1)) # 标准差为0.1的截断正态分布
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) # 初始化为0
输出结果:
[[[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
...
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]]
[[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
...
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]]
[[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
...
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]]
[[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
...
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]]
[[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
...
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]]]
[5 0 4 1 9]
(60000, 28, 28)
(60000,)
tf.Tensor(0.0, shape=(), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor(1.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(0, shape=(), dtype=int32) tf.Tensor(9, shape=(), dtype=int32)
train 函数
def train(epoch): # 训练
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_db): # 每一批样本遍历
# 把x平铺 [256, 28, 28] => [256, 784]
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 784])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # 自动求解
# 第一个隐层 [256, 784] => [256, 256]
# [256, 784]@[784, 256] + [256] => [256, 256] + [256] => [256, 256] + [256, 256] (广播机制)
h1 = x @ w1 + tf.broadcast_to(b1, [x.shape[0], 256])
h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1) # relu激活
# 第二个隐层 [256, 256] => [256, 128]
h2 = h1 @ w2 + b2
h2 = tf.nn.relu(h2) # relu激活
# 输出层 [256, 128] => [128, 10]
out = h2 @ w3 + b3
# 计算损失MSE(Mean Square Error)
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10) # 转换成one_hot编码
loss = tf.square(y_onehot - out) # 计算总误差
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss) # 计算平均误差MSE
# 计算梯度
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3])
# 更新权重
w1.assign_sub(learning_rate * grads[0]) # 自减梯度*学习率
b1.assign_sub(learning_rate * grads[1]) # 自减梯度*学习率
w2.assign_sub(learning_rate * grads[2]) # 自减梯度*学习率
b2.assign_sub(learning_rate * grads[3]) # 自减梯度*学习率
w3.assign_sub(learning_rate * grads[4]) # 自减梯度*学习率
b3.assign_sub(learning_rate * grads[5]) # 自减梯度*学习率
if step % 100 == 0: # 每运行100个批次, 输出一次
print("epoch:", epoch, "step:", step, "loss:", float(loss))
run 函数
def run():
for i in range(iteration_num): # 迭代20次
train(i)
完整代码
import tensorflow as tf
# 定义超参数
batch_size = 256 # 一次训练的样本数目
learning_rate = 0.001 # 学习率
iteration_num = 20 # 迭代次数
# 读取mnist数据集
(x, y), _ = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data() # 读取训练集的特征值和目标值
print(x[:5]) # 调试输出前5个图
print(y[:5]) # 调试输出前5个目标值数字
print(x.shape) # (60000, 28, 28) 单通道
print(y.shape) # (60000,)
# 转换成常量tensor
x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255 # 转换为0~1的形式
y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y, dtype=tf.int32) # 转换为整数形式
# 调试输出范围
print(tf.reduce_min(x), tf.reduce_max(x)) # 0~1
print(tf.reduce_min(y), tf.reduce_max(y)) # 0~9
# 分割数据集
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x, y)).batch(batch_size) # 256为一个batch
train_iter = iter(train_db) # 生成迭代对象
# 定义权重和bias [256, 784] => [256, 256] => [256, 128] => [128, 10]
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([784, 256], stddev=0.1)) # 标准差为0.1的截断正态分布
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256])) # 初始化为0
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([256, 128], stddev=0.1)) # 标准差为0.1的截断正态分布
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([128])) # 初始化为0
w3 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([128, 10], stddev=0.1)) # 标准差为0.1的截断正态分布
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) # 初始化为0
def train(epoch): # 训练
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_db): # 每一批样本遍历
# 把x平铺 [256, 28, 28] => [256, 784]
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 784])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # 自动求解
# 第一个隐层 [256, 784] => [256, 256]
# [256, 784]@[784, 256] + [256] => [256, 256] + [256] => [256, 256] + [256, 256] (广播机制)
h1 = x @ w1 + tf.broadcast_to(b1, [x.shape[0], 256])
h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1) # relu激活
# 第二个隐层 [256, 256] => [256, 128]
h2 = h1 @ w2 + b2
h2 = tf.nn.relu(h2) # relu激活
# 输出层 [256, 128] => [128, 10]
out = h2 @ w3 + b3
# 计算损失MSE(Mean Square Error)
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10) # 转换成one_hot编码
loss = tf.square(y_onehot - out) # 计算总误差
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss) # 计算平均误差MSE
# 计算梯度
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3])
# 更新权重
w1.assign_sub(learning_rate * grads[0]) # 自减梯度*学习率
b1.assign_sub(learning_rate * grads[1]) # 自减梯度*学习率
w2.assign_sub(learning_rate * grads[2]) # 自减梯度*学习率
b2.assign_sub(learning_rate * grads[3]) # 自减梯度*学习率
w3.assign_sub(learning_rate * grads[4]) # 自减梯度*学习率
b3.assign_sub(learning_rate * grads[5]) # 自减梯度*学习率
if step % 100 == 0: # 每运行100个批次, 输出一次
print("epoch:", epoch, "step:", step, "loss:", float(loss))
def run():
for i in range(iteration_num): # 迭代20次
train(i)
if __name__ == "__main__":
run()
输出结果:
epoch: 0 step: 0 loss: 0.5439826250076294
epoch: 0 step: 100 loss: 0.2263326346874237
epoch: 0 step: 200 loss: 0.19458135962486267
epoch: 1 step: 0 loss: 0.1788959801197052
epoch: 1 step: 100 loss: 0.15782299637794495
epoch: 1 step: 200 loss: 0.1580992043018341
epoch: 2 step: 0 loss: 0.15085121989250183
epoch: 2 step: 100 loss: 0.1432340145111084
epoch: 2 step: 200 loss: 0.14373672008514404
epoch: 3 step: 0 loss: 0.13810500502586365
epoch: 3 step: 100 loss: 0.13337770104408264
epoch: 3 step: 200 loss: 0.1334681361913681
epoch: 4 step: 0 loss: 0.12887853384017944
epoch: 4 step: 100 loss: 0.12551936507225037
epoch: 4 step: 200 loss: 0.125375896692276
epoch: 5 step: 0 loss: 0.12160968780517578
epoch: 5 step: 100 loss: 0.1190723180770874
epoch: 5 step: 200 loss: 0.11880680173635483
epoch: 6 step: 0 loss: 0.11563797295093536
epoch: 6 step: 100 loss: 0.11367204040288925
epoch: 6 step: 200 loss: 0.11331651359796524
epoch: 7 step: 0 loss: 0.11063456535339355
epoch: 7 step: 100 loss: 0.10906648635864258
epoch: 7 step: 200 loss: 0.10866570472717285
epoch: 8 step: 0 loss: 0.10636782646179199
epoch: 8 step: 100 loss: 0.10510052740573883
epoch: 8 step: 200 loss: 0.10468046367168427
epoch: 9 step: 0 loss: 0.10268573462963104
epoch: 9 step: 100 loss: 0.10163718461990356
epoch: 9 step: 200 loss: 0.10121693462133408
epoch: 10 step: 0 loss: 0.09949333965778351
epoch: 10 step: 100 loss: 0.09859145432710648
epoch: 10 step: 200 loss: 0.09819269925355911
epoch: 11 step: 0 loss: 0.0966767817735672
epoch: 11 step: 100 loss: 0.09586615860462189
epoch: 11 step: 200 loss: 0.09550992399454117
epoch: 12 step: 0 loss: 0.09417577087879181
epoch: 12 step: 100 loss: 0.09341947734355927
epoch: 12 step: 200 loss: 0.09310202300548553
epoch: 13 step: 0 loss: 0.09193204343318939
epoch: 13 step: 100 loss: 0.09122277796268463
epoch: 13 step: 200 loss: 0.09092779457569122
epoch: 14 step: 0 loss: 0.0899026170372963
epoch: 14 step: 100 loss: 0.08923697471618652
epoch: 14 step: 200 loss: 0.08895798027515411
epoch: 15 step: 0 loss: 0.08804921805858612
epoch: 15 step: 100 loss: 0.08742769062519073
epoch: 15 step: 200 loss: 0.0871589332818985
epoch: 16 step: 0 loss: 0.08635203540325165
epoch: 16 step: 100 loss: 0.0857706069946289
epoch: 16 step: 200 loss: 0.0855005756020546
epoch: 17 step: 0 loss: 0.08479145169258118
epoch: 17 step: 100 loss: 0.08423925191164017
epoch: 17 step: 200 loss: 0.08396687358617783
epoch: 18 step: 0 loss: 0.08334997296333313
epoch: 18 step: 100 loss: 0.08281457424163818
epoch: 18 step: 200 loss: 0.08254452794790268
epoch: 19 step: 0 loss: 0.08201286941766739
epoch: 19 step: 100 loss: 0.08149122446775436
epoch: 19 step: 200 loss: 0.08122102916240692
到此这篇关于详解TensorFlow2实现前向传播的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关TensorFlow2前向传播内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
您可能感兴趣的文章:- 手把手教你使用TensorFlow2实现RNN
- tensorflow2.0实现复杂神经网络(多输入多输出nn,Resnet)
- windows系统Tensorflow2.x简单安装记录(图文)
- TensorFlow2基本操作之合并分割与统计
- Python强化练习之Tensorflow2 opp算法实现月球登陆器
 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服