开始
这是去年的问题了,今天在整理邮件的时候才发现这个问题,感觉顶有意思的,特记录下来。
在表RelationGraph中,有三个字段(ID,Node,RelatedNode),其中Node和RelatedNode两个字段描述两个节点的连接关系;现在要求,找出从节点"p"至节点"j",最短路径(即经过的节点最少)。
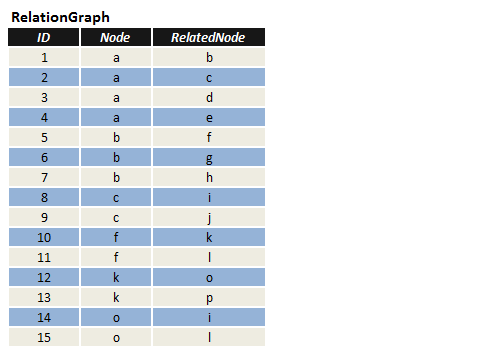
图1.
解析:
了能够更好的描述表RelationGraph中字段Node和 RelatedNode的关系,我在这里特意使用一个图形来描述,
如图2.
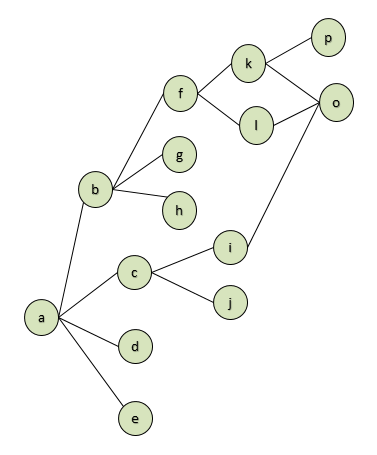
图2.
在图2,可清晰的看出各个节点直接如何相连,也可以清楚的看出节点"p"至节点"j"的的几种可能路径。
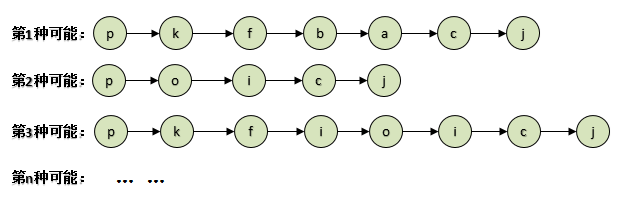
从上面可以看出第2种可能路径,经过的节点最少。
为了解决开始的问题,我参考了两种方法,
第1方法是,
参考单源最短路径算法:Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法,主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。
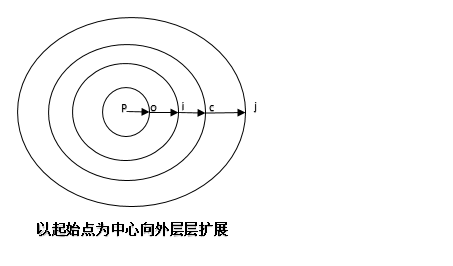
图3.
第2方法是,
针对第1种方法的改进,就是采用多源点方法,这里就是以节点"p"和节点"j"为中心向外层扩展,直到两圆外切点,如图4. :
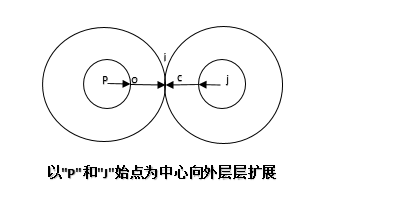
图4.
实现:
在接下来,我就描述在SQL Server中,如何实现。当然我这里采用的前面说的第2种方法,以"P"和"J"为始点像中心外层层扩展。
这里提供有表RelactionGraph的create Insert数据的脚本:
复制代码 代码如下:
use TestDB
go
if object_id('RelactionGraph') Is not null drop table RelactionGraph
create table RelactionGraph(ID int identity,Item nvarchar(50),RelactionItem nvarchar(20),constraint PK_RelactionGraph primary key(ID))
go
create nonclustered index IX_RelactionGraph_Item on RelactionGraph(Item) include(RelactionItem)
create nonclustered index IX_RelactionGraph_RelactionItem on RelactionGraph(RelactionItem) include(Item)
go
insert into RelactionGraph (Item, RelactionItem ) values
('a','b'),('a','c'),('a','d'),('a','e'),
('b','f'),('b','g'),('b','h'),
('c','i'),('c','j'),
('f','k'),('f','l'),
('k','o'),('k','p'),
('o','i'),('o','l')
go
编写一个存储过程up_GetPath
复制代码 代码如下:
use TestDB
go
--Procedure:
if object_id('up_GetPath') Is not null
Drop proc up_GetPath
go
create proc up_GetPath
(
@Node nvarchar(50),
@RelatedNode nvarchar(50)
)
As
set nocount on
declare
@level smallint =1, --当前搜索的深度
@MaxLevel smallint=100, --最大可搜索深度
@Node_WhileFlag bit=1, --以@Node作为中心进行搜索时候,作为能否循环搜索的标记
@RelatedNode_WhileFlag bit=1 --以@RelatedNode作为中心进行搜索时候,作为能否循环搜索的标记
--如果直接找到两个Node存在直接关系就直接返回
if Exists(select 1 from RelationGraph where (Node=@Node And RelatedNode=@RelatedNode) or (Node=@RelatedNode And RelatedNode=@Node) ) or @Node=@RelatedNode
begin
select convert(nvarchar(2000),@Node + ' --> '+ @RelatedNode) As RelationGraphPath,convert(smallint,0) As StopCount
return
end
--
if object_id('tempdb..#1') Is not null Drop Table #1 --临时表#1,存储的是以@Node作为中心向外扩展的各节点数据
if object_id('tempdb..#2') Is not null Drop Table #2 --临时表#2,存储的是以@RelatedNode作为中心向外扩展的各节点数据
create table #1(
Node nvarchar(50),--相对源点
RelatedNode nvarchar(50), --相对目标
Level smallint --深度
)
create table #2(Node nvarchar(50),RelatedNode nvarchar(50),Level smallint)
insert into #1 ( Node, RelatedNode, Level )
select Node, RelatedNode, @level from RelationGraph a where a.Node =@Node union --正向:以@Node作为源查询
select RelatedNode, Node, @level from RelationGraph a where a.RelatedNode = @Node --反向:以@Node作为目标进行查询
set @Node_WhileFlag=sign(@@rowcount)
insert into #2 ( Node, RelatedNode, Level )
select Node, RelatedNode, @level from RelationGraph a where a.Node =@RelatedNode union --正向:以@RelatedNode作为源查询
select RelatedNode, Node, @level from RelationGraph a where a.RelatedNode = @RelatedNode --反向:以@RelatedNode作为目标进行查询
set @RelatedNode_WhileFlag=sign(@@rowcount)
--如果在表RelationGraph中找不到@Node 或 @RelatedNode 数据,就直接跳过后面的While过程
if not exists(select 1 from #1) or not exists(select 1 from #2)
begin
goto While_Out
end
while not exists(select 1 from #1 a inner join #2 b on b.RelatedNode=a.RelatedNode) --判断是否出现切点
and (@Node_WhileFlag|@RelatedNode_WhileFlag)>0 --判断是否能搜索
And @level@MaxLevel --控制深度
begin
if @Node_WhileFlag >0
begin
insert into #1 ( Node, RelatedNode, Level )
--正向
select a.Node,a.RelatedNode,@level+1
From RelationGraph a
where exists(select 1 from #1 where RelatedNode=a.Node And Level=@level) And
Not exists(select 1 from #1 where Node=a.Node)
union
--反向
select a.RelatedNode,a.Node,@level+1
From RelationGraph a
where exists(select 1 from #1 where RelatedNode=a.RelatedNode And Level=@level) And
Not exists(select 1 from #1 where Node=a.RelatedNode)
set @Node_WhileFlag=sign(@@rowcount)
end
if @RelatedNode_WhileFlag >0
begin
insert into #2 ( Node, RelatedNode, Level )
--正向
select a.Node,a.RelatedNode,@level+1
From RelationGraph a
where exists(select 1 from #2 where RelatedNode=a.Node And Level=@level) And
Not exists(select 1 from #2 where Node=a.Node)
union
--反向
select a.RelatedNode,a.Node,@level+1
From RelationGraph a
where exists(select 1 from #2 where RelatedNode=a.RelatedNode And Level=@level) And
Not exists(select 1 from #2 where Node=a.RelatedNode)
set @RelatedNode_WhileFlag=sign(@@rowcount)
end
select @level+=1
end
While_Out:
--下面是构造返回的结果路径
if object_id('tempdb..#Path1') Is not null Drop Table #Path1
if object_id('tempdb..#Path2') Is not null Drop Table #Path2
;with cte_path1 As
(
select a.Node,a.RelatedNode,Level,convert(nvarchar(2000),a.Node+' -> '+a.RelatedNode) As RelationGraphPath,Convert(smallint,1) As PathLevel From #1 a where exists(select 1 from #2 where RelatedNode=a.RelatedNode)
union all
select b.Node,a.RelatedNode,b.Level,convert(nvarchar(2000),b.Node+' -> '+a.RelationGraphPath) As RelationGraphPath ,Convert(smallint,a.PathLevel+1) As PathLevel
from cte_path1 a
inner join #1 b on b.RelatedNode=a.Node
and b.Level=a.Level-1
)
select * Into #Path1 from cte_path1
;with cte_path2 As
(
select a.Node,a.RelatedNode,Level,convert(nvarchar(2000),a.Node) As RelationGraphPath,Convert(smallint,1) As PathLevel From #2 a where exists(select 1 from #1 where RelatedNode=a.RelatedNode)
union all
select b.Node,a.RelatedNode,b.Level,convert(nvarchar(2000),a.RelationGraphPath+' -> '+b.Node) As RelationGraphPath ,Convert(smallint,a.PathLevel+1)
from cte_path2 a
inner join #2 b on b.RelatedNode=a.Node
and b.Level=a.Level-1
)
select * Into #Path2 from cte_path2
;with cte_result As
(
select a.RelationGraphPath+' -> '+b.RelationGraphPath As RelationGraphPath,a.PathLevel+b.PathLevel -1 As StopCount,rank() over(order by a.PathLevel+b.PathLevel) As Result_row
From #Path1 a
inner join #Path2 b on b.RelatedNode=a.RelatedNode
and b.Level=1
where a.Level=1
)
select distinct RelationGraphPath,StopCount From cte_result where Result_row=1
go
上面的存储过程,主要分为两大部分,第1部分是实现如何搜索,第2部分实现如何构造返回结果。其中第1部分的代码根据前面的方法2,通过@Node 和 @RelatedNode 两个节点向外层搜索,每次搜索返回的节点都保存至临时表#1和#2,再判断临时表#1和#2有没有出现切点,如果出现就说明已找到最短的路径(经过多节点数最少),否则就继续循环搜索,直到循环至最大的搜索深度(@MaxLevel smallint=100)或找到切点。要是到100层都没搜索到切点,将放弃搜索。这里使用最大可搜索深度@MaxLevel,目的是控制由于数据量大可能会导致性能差,因为在这里数据量与搜索性能成反比。代码中还说到一个正向和反向搜索,主要是相对Node 和 RelatedNode来说,它们两者互为参照对象,进行向外搜索使用。
下面是存储过程的执行:
复制代码 代码如下:
use TestDB
go
exec dbo.up_GetPath
@Node = 'p',
@RelatedNode = 'j'
go
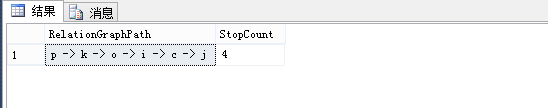
你可以根据需要来,赋予@Node 和 @RelatedNode不同的值。
拓展:
前面的例子,可扩展至城市的公交路线,提供两个站点,搜索经过这两个站点最少站点公交路线;可以扩展至社区的人际关系的搜索,如一个人与另一个人想认识,那么他们直接要经过多少个人才可以。除了人与人直接有直接的朋友、亲戚关联,还可以通过人与物有关联找到人与人关联,如几个作家通过出版一个本,那么就说明这几个人可以通过某一本书的作者列表中找到他们存在共同出版书籍的关联,这为搜索两个人认识路径提供参考。这问题可能会非常大复杂,但可以这样的扩展。
小结:
这里只是找两个节点的所有路径中,节点数最少的路径,在实际的应用中,可能会碰到比这里更复杂的情况。在其他的环境或场景可能会带有长度,时间,多节点,多作用域等一些信息。无论如何,一般都要参考一些原理,算法来实现。
您可能感兴趣的文章:- SQLServer地址搜索性能优化
- 在SQL Server 2005所有表中搜索某个指定列的方法
- sqlserver中在指定数据库的所有表的所有列中搜索给定的值
- SQL Server 全文搜索功能介绍
 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服