| 解析器 | 使用方法 | 条件 |
|---|---|---|
| bs4的html解析器 | BeautifulSoup(demo,‘html.parser') | 安装bs4库 |
| lxml的html解析器 | BeautifulSoup(demo,‘lxml') | pip install lxml |
| lxml的xml解析器 | BeautifulSoup(demo,‘xml') | pip install lxml |
| html5lib的解析器 | BeautifulSoup(demo,‘html5lib') | pip install html5lib |
假如有一个简单的网页,提取百度搜索页面的一部分源代码为例
!DOCTYPE html> html> head> meta content="text/html;charset=utf-8" http-equiv="content-type" /> meta content="IE=Edge" http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" /> meta content="always" name="referrer" /> link href="https://ss1.bdstatic.com/5eN1bjq8AAUYm2zgoY3K/r/www/cache/bdorz/baidu.min. css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" /> title>百度一下,你就知道 /title> /head> body link="#0000cc"> div > div > div > div > a href="http://news.baidu.com" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" name="tj_trnews">新闻 /a> a href="https://www.hao123.com" rel="external nofollow" name="tj_trhao123">hao123 /a> a href="http://map.baidu.com" rel="external nofollow" name="tj_trmap">地图 /a> a href="http://v.baidu.com" rel="external nofollow" name="tj_trvideo">视频 /a> a href="http://tieba.baidu.com" rel="external nofollow" name="tj_trtieba">贴吧 /a> a href="//www.baidu.com/more/" rel="external nofollow" name="tj_briicon" >更多产品 /a> /div> /div> /div> /div> /body> /html>
结合requests库和使用BeautifulSoup库的html解析器,对其进行解析有如下
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 使用Requests库加载页面代码
r = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com')
r.raise_for_status() # 状态码返回
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
demo = r.text
# 使用BeautifulSoup库解析代码
soup = BeautifulSoup(demo,'html.parser') # 使用html的解析器
print(soup.prettify()) # prettify 方式输出页面

BeautifulSoup4将复杂HTML文档转换成一个复杂的树形结构,每个节点都是Python对象,BeautifulSoup库有针对于html的标签数的特定元素,重点有如下三种
p > ... /p>
| 基本元素 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Tag | 标签,最基本的信息组织单元,分别用>和/>标明开头和结尾,格式:soup.a或者soup.p(获取a标签中或者p标签中的内容) |
| Name | 标签的名字,
… 的名字是‘p' 格式为:.name |
| Attributes | 标签的属性,字典形式组织,格式:.attrs |
| NavigableString | 标签内非属性字符串,>…/>中的字符串,格式:.string |
| Comment | 标签内的字符串的注释部分,一种特殊的Comment类型 |
标签是html中的最基本的信息组织单元,使用方式如下
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = 'https://www.baidu.com' bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser") print(bs.title) # 获取title标签的所有内容 print(bs.head) # 获取head标签的所有内容 print(bs.a) # 获取第一个a标签的所有内容 print(type(bs.a)) # 类型
在Tag标签中最重要的就是html页面中的name哈attrs属性,使用方式如下
print(bs.name)
print(bs.head.name) # head 之外对于其他内部标签,输出的值便为标签本身的名称
print(bs.a.attrs) # 把 a 标签的所有属性打印输出了出来,得到的类型是一个字典。
print(bs.a['class']) # 等价 bs.a.get('class') 也可以使用get方法,传入属性的名称,二者是等价的
bs.a['class'] = "newClass" # 对这些属性和内容进行修改
print(bs.a)
del bs.a['class'] # 对这个属性进行删除
print(bs.a)
NavigableString中的string方法用于获取标签内部的文字
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = 'https://www.baidu.com' bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser") print(bs.title.string) print(type(bs.title.string))
Comment 对象是一个特殊类型的 NavigableString 对象,其输出的内容不包括注释符号,用于输出注释中的内容
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = 'https://www.baidu.com' bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser") print(bs.a) # 标签中的内容a href="http://news.baidu.com" rel="external nofollow" rel="external nofollow" name="tj_trnews">!--新闻-->/a> print(bs.a.string) # 新闻 print(type(bs.a.string)) # class 'bs4.element.Comment'>
在HTML中有如下特定的基本格式,也是构成HTML页面的基本组成成分
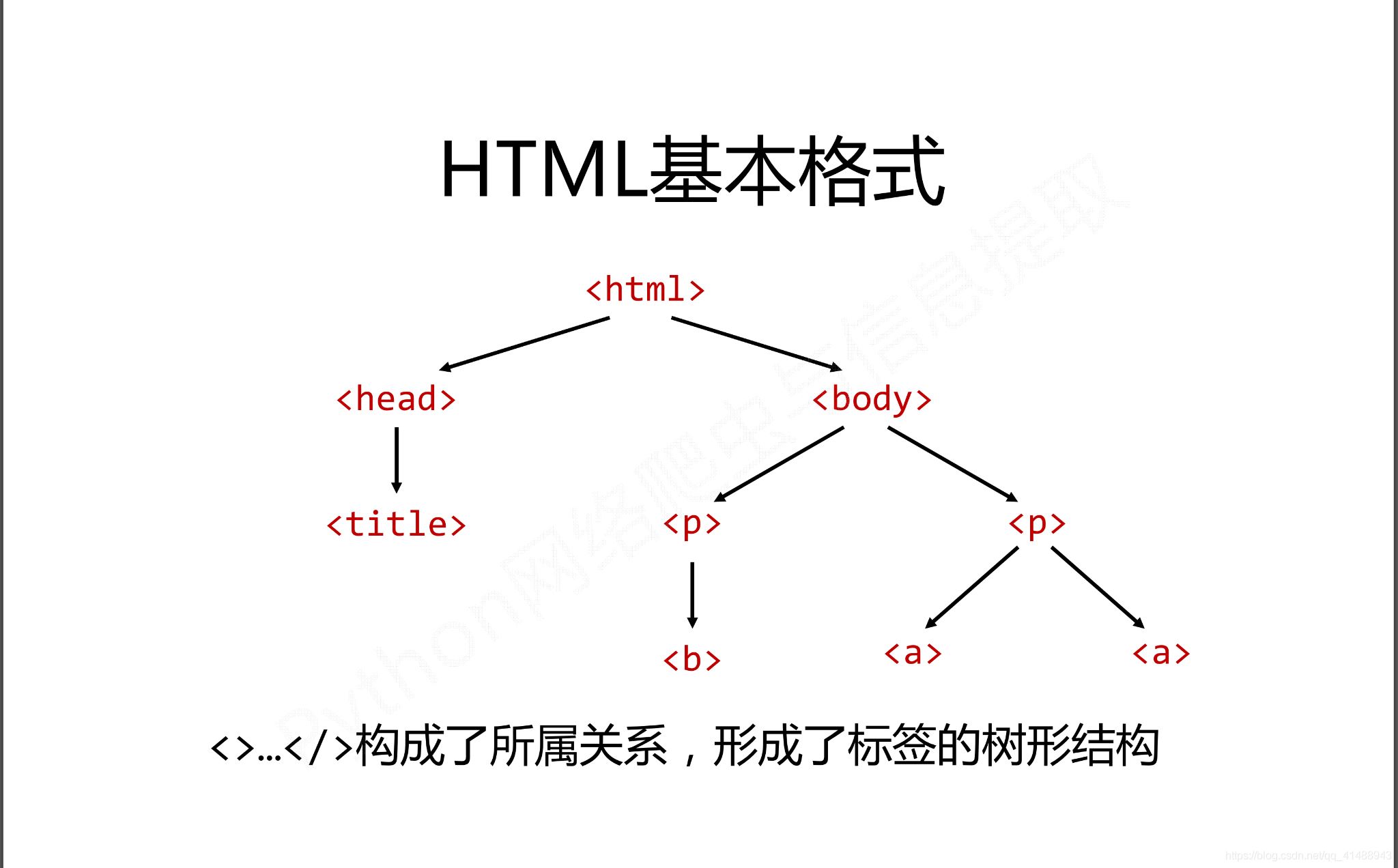
而在这种基本的格式下有三种基本的遍历流程
三种种遍历方式分别是从当前节点出发。对之上或者之下或者平行的格式以及关系进行遍历
下行遍历有三种遍历的属性,分别是
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .contents | 子节点的列表,将所有儿子节点存入列表 |
| .children | 子节点的迭代类型,用于循环遍历儿子节点 |
| .descendants | 子孙节点的迭代类型,包含所有子孙节点,用于循环遍历 |
使用举例
soup = BeautifulSoup(demo,'html.parser') # 循环遍历儿子节点 for child in soup.body.children: print(child) # 循环遍历子孙节点 for child in soup.body.descendants: print(child) # 输出子节点的列表形式 print(soup.head.contents) print(soup.head.contents[1]) # 用列表索引来获取它的某一个元素
上行遍历有两种方式
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .parent | 节点的父亲标签 |
| .parents | 节点先辈标签的迭代类型,用于循环遍历先辈节点,返回一个生成器 |
soup = BeautifulSoup(demo,'html.parser') for parent in soup.a.parents: if parent is None: parent(parent) else: print(parent.name)
平行遍历有四种属性
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .next_sibling | 返回按照HTML文本顺序的下一个平行节点标签 |
| .previous_sibling | 返回按照HTML文本顺序的上一个平行节点标签 |
| .next_siblings | 迭代类型,返回按照html文本顺序的后续所有平行节点标签 |
| .previous_siblings | 迭代类型,返回按照html文本顺序的前序所有平行节点标签 |
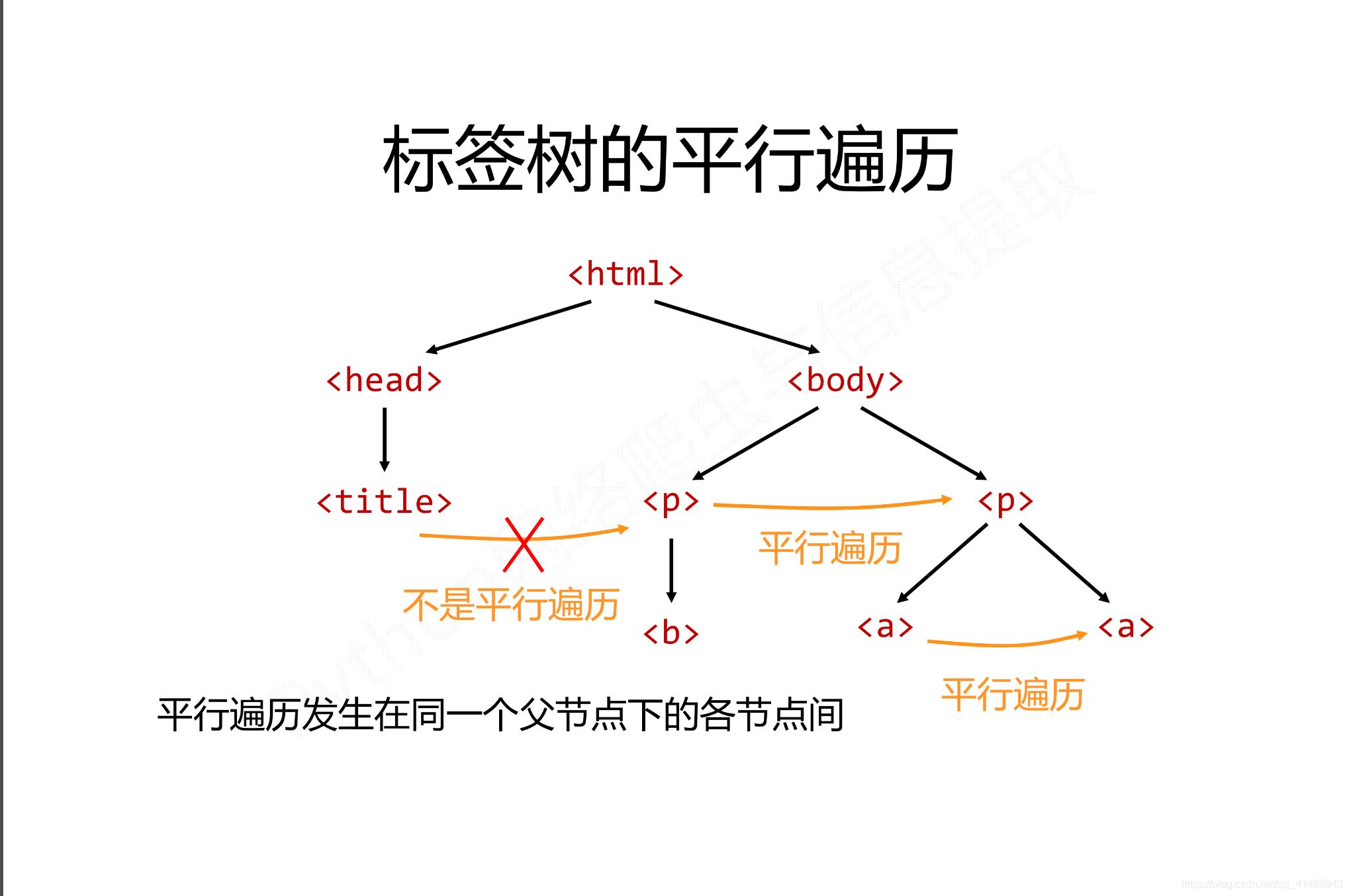
平行遍历举例如下
for sibling in soup.a.next_sibling: print(sibling) # 遍历后续节点 for sibling in soup.a.previous_sibling: print(sibling) # 遍历
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .strings | 如果Tag包含多个字符串,即在子孙节点中有内容,可以用此获取,而后进行遍历 |
| .stripped_strings | 与strings用法一致,可以去除掉那些多余的空白内容 |
| .has_attr | 判断Tag是否包含属性 |
使用soup.find_all(name,attrs,recursive,string,**kwargs)方法,用于返回一个列表类型,存储查找的结果
如果是指定的字符串:会查找与字符串完全匹配的内容,如下
a_list = bs.find_all("a")
print(a_list) # 将会返回所有包含a标签的内容
如果是使用正则表达式:将会使用BeautifulSoup4中的search()方法来匹配内容,如下
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
html = 'https://www.baidu.com'
bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser")
t_list = bs.find_all(re.compile("a"))
for item in t_list:
print(item) # 输出列表
如果传入一个列表:BeautifulSoup4将会与列表中的任一元素匹配到的节点返回,如下
t_list = bs.find_all(["meta","link"]) for item in t_list: print(item)
如果传入一个函数或者方法:将会根据函数或者方法来匹配
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = 'https://www.baidu.com'
bs = BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser")
def name_is_exists(tag):
return tag.has_attr("name")
t_list = bs.find_all(name_is_exists)
for item in t_list:
print(item)
并不是所有的属性都可以使用上面这种方式进行搜索,比如HTML的data属性,用于指定属性搜索
t_list = bs.find_all(data-foo="value")
通过通过string参数可以搜索文档中的字符串内容,与name参数的可选值一样,string参数接受字符串,正则表达式,列表
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
html = 'https://www.baidu.com'
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")
t_list = bs.find_all(attrs={"data-foo": "value"})
for item in t_list:
print(item)
t_list = bs.find_all(text="hao123")
for item in t_list:
print(item)
t_list = bs.find_all(text=["hao123", "地图", "贴吧"])
for item in t_list:
print(item)
t_list = bs.find_all(text=re.compile("\d"))
for item in t_list:
print(item)
使用find_all()方法的时,常用到正则表达式的形式import re如下所示
soup.find_all(sring = re.compile('pyhton')) # 指定查找内容
# 或者指定使用正则表达式要搜索的内容
sring = re.compile('pyhton') # 字符为python
soup.find_all(string) # 调用方法模板

此文列举了BeautifulSoup库在爬虫中的基本使用,不正确之处望指教,参考
到此这篇关于python爬虫beautifulsoup库使用操作教程全解(python爬虫基础入门)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python爬虫beautifulsoup库内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服