使用matplotlib绘图时,在弹出的窗口中默认是有工具栏的,那么这些工具栏是如何定义的呢?
工具栏的三种模式
matplotlib的基础配置由运行时参数(rcParams)控制,导入matplotlib时,加载matplotlibrc文件生成默认运行时参数。
查看matplotlibrc文件可知#toolbar: toolbar2 # {None, toolbar2, toolmanager},即工具栏有三种模式None、toolbar2和toolmanager,其中默认模式为toolbar2。
工具栏模式切换
通过类似语句plt.rcParams['toolbar'] = 'None'可控制工具栏的模式。
需要注意的是plt.rcParams['toolbar'] = 'None'应当放置在图像实例化之前。
None模式:禁用工具栏。
plt.rcParams['toolbar'] = 'None'
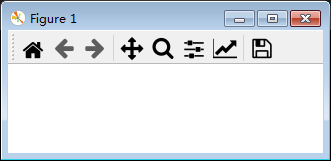
toolbar2模式:默认工具栏布局。
plt.rcParams['toolbar'] = 'toolbar2'
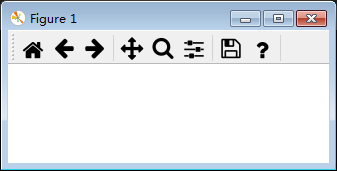
toolmanager模式:工具栏布局模式与toolbar2模式稍有不同。
plt.rcParams['toolbar'] = 'toolmanager'
工具栏模式切换原理
和工具栏相关的模块有:
- matplotlib.backend_bases
- matplotlib.backend_managers
- matplotlib.backend_tools
- matplotlib.backends
工具栏最终依靠后端实现,不同的后端具体实现会有一些差异,我选择的后端是Pyqt5,通过查看模块matplotlib.backends.backend_qt5源码可知,matplotlib在利用后端生成窗口时根据rcParams['toolbar']的值选择不同的工具栏构造方式。
def _get_toolbar(self, canvas, parent):
# must be inited after the window, drawingArea and figure
# attrs are set
if matplotlib.rcParams['toolbar'] == 'toolbar2':
toolbar = NavigationToolbar2QT(canvas, parent, True)
elif matplotlib.rcParams['toolbar'] == 'toolmanager':
toolbar = ToolbarQt(self.toolmanager, self.window)
else:
toolbar = None
return toolbar
默认模式(toolbar2)原理
与该模式相关的重要定义有:
matplotlib.backend_bases.NavigationToolbar2(canvas)类:默认的toolbar2模式工具栏的基类,后端需要通过canvas对象处理工具栏按钮事件、覆盖构造方法初始化工具栏、覆盖save_figure()等方法。matplotlib.backends.backend_qt5.NavigationToolbar2QT(NavigationToolbar2, QtWidgets.QToolBar)类:定义了QT后端默认模式工具栏的具体实现。matplotlib.backend_bases.FigureCanvasBase类:canvas对象的基类,通过toolbar属性与工具栏进行连接。matplotlib.backend_bases.NavigationToolbar2(canvas).toolitems属性:定义了默认模式工具栏工具项列表。
案例:验证默认模式工具栏布局
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig=plt.gcf()
toolbar = fig.canvas.manager.toolbar
print(toolbar.toolitems)
输出:
[('Home', 'Reset original view', 'home', 'home'),
('Back', 'Back to previous view', 'back', 'back'),
('Forward', 'Forward to next view', 'forward', 'forward'),
(None, None, None, None),
('Pan', 'Left button pans, Right button zooms\nx/y fixes axis, CTRL fixes aspect', 'move', 'pan'),
('Zoom', 'Zoom to rectangle\nx/y fixes axis, CTRL fixes aspect', 'zoom_to_rect', 'zoom'),
('Subplots', 'Configure subplots', 'subplots', 'configure_subplots'),
('Customize', 'Edit axis, curve and image parameters', 'qt4_editor_options', 'edit_parameters'),
(None, None, None, None),
('Save', 'Save the figure', 'filesave', 'save_figure')]
根据源码可知,列表中每个元组为工具项定义,元组的四个元素分别表示按钮名称、按钮提示文本、按钮图像、按钮对应方法。
# list of toolitems to add to the toolbar, format is:
# (
# text, # the text of the button (often not visible to users)
# tooltip_text, # the tooltip shown on hover (where possible)
# image_file, # name of the image for the button (without the extension)
# name_of_method, # name of the method in NavigationToolbar2 to call
# )
工具栏管理器模式(toolmanager)原理
与该模式相关的重要定义有:
matplotlib.backend_bases.ToolContainerBase(toolmanager)类:工具栏容器的基类,定义了工具栏编辑的方法。构造函数参数为toolmanager,表示工具栏容器容纳的工具栏。matplotlib.backend_managers.ToolManager(figure=None)类:管理用户触发工具栏工具项按钮而产生的动作。matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolBase类:所有工具栏工具项的基类,所有工具项均由matplotlib.backend_managers.ToolManager实例化。matplotlib.backend_tools.default_tools变量:字典类型,实例化基于matplotlib.backend_tools.ToolBase类定义的内置工具项。matplotlib.backend_tools.default_toolbar_tools变量:嵌套列表,以类似格式[[分组1, [工具1, 工具2 ...]], [分组2, [...]]]定义工具栏布局。matplotlib.backend_tools.add_tools_to_container函数:设置toolbarmanager模式默认工具栏。
案例:验证工具栏管理器模式工具栏布局
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['toolbar'] = 'toolmanager'
fig=plt.gcf()
toolbar= fig.canvas.manager.toolbar
print(toolbar._toolitems)
输出:
{'home': [(PyQt5.QtWidgets.QToolButton object at 0x00000289EABBC1F8>, function ToolbarQt.add_toolitem.locals>.handler at 0x00000289EB0BC510>)],
'back': [(PyQt5.QtWidgets.QToolButton object at 0x00000289EAE86678>, function ToolbarQt.add_toolitem.locals>.handler at 0x00000289EB0BC598>)],
'forward': [(PyQt5.QtWidgets.QToolButton object at 0x00000289EAE8B4C8>, function ToolbarQt.add_toolitem.locals>.handler at 0x00000289EB0BC620>)],
'pan': [(PyQt5.QtWidgets.QToolButton object at 0x00000289EAE8BAF8>, function ToolbarQt.add_toolitem.locals>.handler at 0x00000289EB0BC6A8>)],
'zoom': [(PyQt5.QtWidgets.QToolButton object at 0x00000289EAE93DC8>, function ToolbarQt.add_toolitem.locals>.handler at 0x00000289EB0BC7B8>)],
'subplots': [(PyQt5.QtWidgets.QToolButton object at 0x00000289EAE93438>, function ToolbarQt.add_toolitem.locals>.handler at 0x00000289EB0BC8C8>)],
'save': [(PyQt5.QtWidgets.QToolButton object at 0x00000289EAE93678>, function ToolbarQt.add_toolitem.locals>.handler at 0x00000289EB0BC950>)],
'help': [(PyQt5.QtWidgets.QToolButton object at 0x00000289EAE93A68>, function ToolbarQt.add_toolitem.locals>.handler at 0x00000289EB0BC9D8>)]}
到此这篇关于pytho matplotlib工具栏源码探析一之禁用工具栏、默认工具栏和工具栏管理器三种模式的差异的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关pytho matplotlib工具栏内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
您可能感兴趣的文章:- python matplotlib工具栏源码探析二之添加、删除内置工具项的案例
- python matplotlib工具栏源码探析三之添加、删除自定义工具项的案例详解
- 详解python安装matplotlib库三种失败情况
- Python matplotlib读取excel数据并用for循环画多个子图subplot操作
 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服