目录
- 一、列表结构体
- 二、创建列表
- 三、添加元素
- 四、移除元素
- 五、清空
- 六、销毁
一、列表结构体
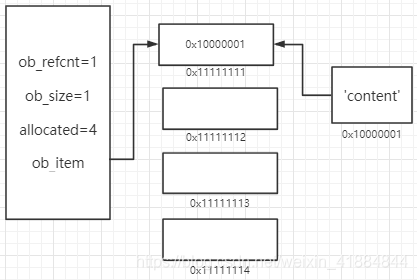
创建列表C语言底层的结构体
lists = []
list.append('name')
list.append('age')
list.append('grade')
typedef struct{
struct _object *_ob_next;
struct _object *_ob_prev; // python内部将对象放在链表进行内存管理
Py_ssize_t ob_refcnt; // 引用计数器,就是多少变量用了它
PyObject **ob_item; // 指针的指针,存列表的元素
Py_ssize_t ob_size; // 已有元素个数
Py_ssize_t allocated; // 列表容量,可容纳个数
} PyListObject;
c源码来自 listobject.c
二、创建列表
name_list = [ ]
PyObject *
PyList_New(Py_ssize_t size)
{
PyListObject *op;
size_t nbytes;
#ifdef SHOW_ALLOC_COUNT
static int initialized = 0;
if (!initialized) {
Py_AtExit(show_alloc);
initialized = 1;
}
#endif
// 缓存机制
if (size 0) {
PyErr_BadInternalCall();
return NULL;
}
/* Check for overflow without an actual overflow,
* which can cause compiler to optimise out */
if ((size_t)size > PY_SIZE_MAX / sizeof(PyObject *))
return PyErr_NoMemory();
nbytes = size * sizeof(PyObject *);
if (numfree) {
numfree--;
op = free_list[numfree];
_Py_NewReference((PyObject *)op);
#ifdef SHOW_ALLOC_COUNT
count_reuse++;
#endif
} else {
op = PyObject_GC_New(PyListObject, PyList_Type);
if (op == NULL)
return NULL;Py
#ifdef SHOW_ALLOC_COUNT
count_alloc++;
#endif
}
if (size = 0)
op->ob_item = NULL;
else {
op->ob_item = (PyObject **) PyMem_MALLOC(nbytes);
if (op->ob_item == NULL) {
Py_DECREF(op);
return PyErr_NoMemory();
}
memset(op->ob_item, 0, nbytes);
}
Py_SIZE(op) = size; // 元素个数
op->allocated = size; // 容量
_PyObject_GC_TRACK(op); //放到双向链表进行维护
return (PyObject *) op; //返回列表的指针
}
三、添加元素
list中插入一个元素时,扩容连续的内存地址(容量),在内存创建需要插入的内容p,将地址*p放入list的空间中,所以,PyListObject的ob_item是指针的指针
扩容的曲线一般就是0,4,8,16,24…
// 添加元素
static int
app1(PyListObject *self, PyObject *v)
{
// 获取实际元素个数
Py_ssize_t n = PyList_GET_SIZE(self);
assert (v != NULL);
if (n == PY_SSIZE_T_MAX) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_OverflowError,
"cannot add more objects to list");
return -1;
}
// 计算当前容量和内部元素个数
// 直接添加元素/扩容添加
if (list_resize(self, n+1) == -1)
return -1;
// 将元素添加到ob_item,v
Py_INCREF(v);
PyList_SET_ITEM(self, n, v);
return 0;
}
// 扩容机制
// newsize: 已存在元素个数+1
static int
list_resize(PyListObject *self, Py_ssize_t newsize)
{
PyObject **items;
size_t new_allocated;
Py_ssize_t allocated = self->allocated; // 当前的容量
// 1,容量大于个数
// 2,个数大于容量的一半(容量足够且没有内存浪费)
if (allocated >= newsize newsize >= (allocated >> 1)) {
assert(self->ob_item != NULL || newsize == 0);
Py_SIZE(self) = newsize;
return 0;
}
/*
* The growth pattern is: 0, 4, 8, 16, 25, 35, 46, 58, 72, 88, ...
*/
// 扩容机制的算法
new_allocated = (newsize >> 3) + (newsize 9 ? 3 : 6);
/* check for integer overflow */
if (new_allocated > PY_SIZE_MAX - newsize) {
PyErr_NoMemory();
return -1;
} else {
new_allocated += newsize;
}
if (newsize == 0)
new_allocated = 0;
// 扩容/缩容(涉及原来元素的迁移)
items = self->ob_item;
if (new_allocated = (PY_SIZE_MAX / sizeof(PyObject *)))
PyMem_RESIZE(items, PyObject *, new_allocated);
else
items = NULL;
if (items == NULL) {
PyErr_NoMemory();
return -1;
}
// 赋值,更新个数和容量
self->ob_item = items;
Py_SIZE(self) = newsize;
self->allocated = new_allocated;
return 0;
}
四、移除元素
list.pop()
删除最后一个元素只需要修改size,不需要清除数据,下次append可以直接覆盖这个位置
指定索引位置移除后,向前补位
static PyObject *
listpop(PyListObject *self, PyObject *args)
{
Py_ssize_t i = -1;
PyObject *v;
int status;
if (!PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "|n:pop", i))
return NULL;
if (Py_SIZE(self) == 0) {
/* Special-case most common failure cause */
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_IndexError, "pop from empty list");
return NULL;
}
if (i 0)
i += Py_SIZE(self);
if (i 0 || i >= Py_SIZE(self)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_IndexError, "pop index out of range");
return NULL;
}
v = self->ob_item[i];
// 删除最后一个,仅改变size
if (i == Py_SIZE(self) - 1) {
status = list_resize(self, Py_SIZE(self) - 1);
assert(status >= 0);
return v; /* and v now owns the reference the list had */
}
Py_INCREF(v);
// 不是最后一个,需要移动数据位置
status = list_ass_slice(self, i, i+1, (PyObject *)NULL);
assert(status >= 0);
/* Use status, so that in a release build compilers don't
* complain about the unused name.
*/
(void) status;
return v;
}
五、清空
list.clear()
static int
list_clear(PyListObject *a)
{
Py_ssize_t i;
PyObject **item = a->ob_item;
if (item != NULL) {
i = Py_SIZE(a);
// 各个元素设置为空
Py_SIZE(a) = 0;
a->ob_item = NULL;
a->allocated = 0;
// 引用计数器-1
while (--i >= 0) {
Py_XDECREF(item[i]);
}
PyMem_FREE(item);
}
return 0;
}
六、销毁
del list
销毁列表对象的操作
将列表的引用计数-1
引用计数>0,还有应用的话不做操作
引用计数=0,没人使用
- 处理列表的元素,将所有引用计数-1(GC回收0计数)
- ob_item=0,ob_size=0,ob_allocated=0
- 将列表从双向链表移除,可以销毁
- 为了提高效率,Python结束期在内部为free_list缓存80个list,存放无使用的list,再创建的时候直接从缓存中拿来初始化。如果已经存了80个,del 的时候直接在内存中销毁对象
static void
list_dealloc(PyListObject *op)
{
Py_ssize_t i;
// 判断引用计数是否为0
PyObject_GC_UnTrack(op);
Py_TRASHCAN_SAFE_BEGIN(op)
if (op->ob_item != NULL) {
i = Py_SIZE(op);
while (--i >= 0) {
Py_XDECREF(op->ob_item[i]);
}
PyMem_FREE(op->ob_item);
}
// free_list没有80个的话缓存这个list
if (numfree PyList_MAXFREELIST PyList_CheckExact(op))
free_list[numfree++] = op;
else
Py_TYPE(op)->tp_free((PyObject *)op);
Py_TRASHCAN_SAFE_END(op)
}
就是说创建列表时,实际上不会直接开辟内存,而是先看看free_list
# 两次list的地址相同
>>> list1=[1,2,3]
>>> id(list1)
69070216L
>>> del list1
>>> list2=[0,0,0]
>>> id(list2)
69303304L
>>>
到此这篇关于Python源码解析之List的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python List内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
您可能感兴趣的文章:- Python源码学习之PyObject和PyTypeObject
- python源码剖析之PyObject详解
- python opencv人脸识别考勤系统的完整源码
- python 制作手机归属地查询工具(附源码)
- python基于tkinter制作无损音乐下载工具(附源码)
- Python bsonrpc源码解读
- Python源码学习之PyType_Type和PyBaseObject_Type详解
- Python制作脚本帮女朋友抢购清空购物车
 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服