目录
- 一、导入所需的库
- 二、定义可视化函数显示图像上的边界框和类标签
- 三、获取图像和标注
- 四、使用RandomSizedBBoxSafeCrop保留原始图像中的所有边界框
- 五、定义增强管道
- 六、输入用于增强的图像和边框
- 七、其他不同随机种子的示例
一、导入所需的库
import random
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import albumentations as A
二、定义可视化函数显示图像上的边界框和类标签
可视化函数参考https://github.com/facebookresearch/Detectron/blob/master/detectron/utils/vis.py
BOX_COLOR = (255, 0, 0) # Red
TEXT_COLOR = (255, 255, 255) # White
def visualize_bbox(img, bbox, class_name, color=BOX_COLOR, thickness=2):
"""Visualizes a single bounding box on the image"""
x_min, y_min, w, h = bbox
x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max = int(x_min), int(x_min + w), int(y_min), int(y_min + h)
cv2.rectangle(img, (x_min, y_min), (x_max, y_max), color=color, thickness=thickness)
((text_width, text_height), _) = cv2.getTextSize(class_name, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.35, 1)
cv2.rectangle(img, (x_min, y_min - int(1.3 * text_height)), (x_min + text_width, y_min), BOX_COLOR, -1)
cv2.putText(
img,
text=class_name,
org=(x_min, y_min - int(0.3 * text_height)),
fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
fontScale=0.35,
color=TEXT_COLOR,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA,
)
return img
def visualize(image, bboxes, category_ids, category_id_to_name):
img = image.copy()
for bbox, category_id in zip(bboxes, category_ids):
class_name = category_id_to_name[category_id]
img = visualize_bbox(img, bbox, class_name)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(img)
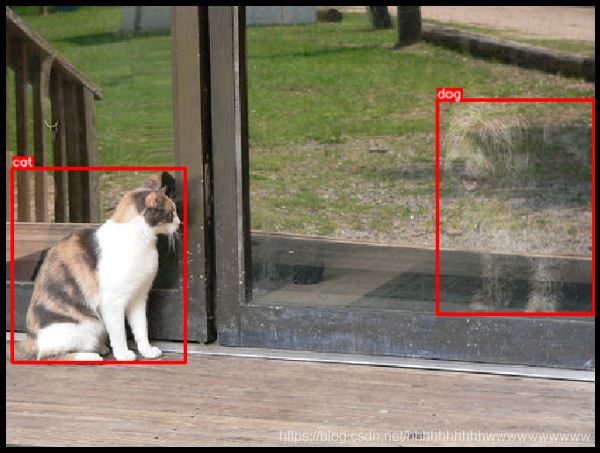
三、获取图像和标注
在此示例中,我们将使用来自COCO数据集的图像,该图像具有两个关联的边界框。 该映像位于http://cocodataset.org/#explore?id=386298
从磁盘加载图像
image = cv2.imread('images/000000386298.jpg')
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
用坐标和类标签定义两个边界框
这些边界框的坐标使用coco格式声明。 每个边界框使用四个值[x_min, y_min, width, height]进行描述。 有关边界框坐标的不同格式的详细说明,请参阅有关边界框的文档文章-https://albumentations.ai/docs/getting_started/bounding_boxes_augmentation/。
bboxes = [[5.66, 138.95, 147.09, 164.88], [366.7, 80.84, 132.8, 181.84]]
category_ids = [17, 18]
# We will use the mapping from category_id to the class name
# to visualize the class label for the bounding box on the image
category_id_to_name = {17: 'cat', 18: 'dog'}
展示图像的边框
visualize(image, bboxes, category_ids, category_id_to_name)
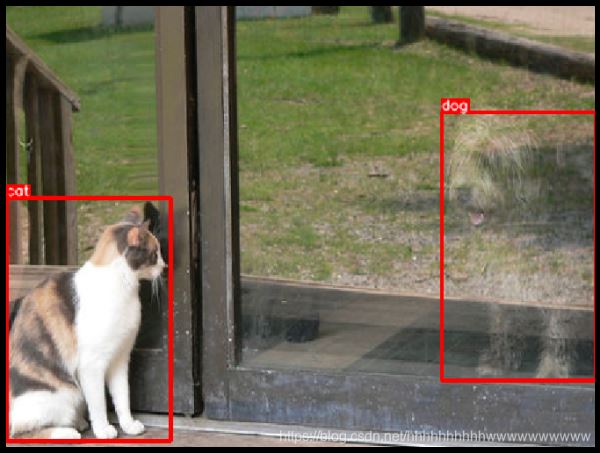
四、使用RandomSizedBBoxSafeCrop保留原始图像中的所有边界框
RandomSizedBBoxSafeCrop crops a random part of the image. It ensures that the cropped part will contain all bounding boxes from the original image. Then the transform rescales the crop to height and width specified by the respective parameters. The erosion_rate parameter controls how much area of the original bounding box could be lost after cropping. erosion_rate = 0.2 means that the augmented bounding box's area could be up to 20% smaller than the area of the original bounding box.
RandomSizedBBoxSafeCrop裁剪图像的随机部分。 它确保裁剪的部分将包含原始图像的所有边界框。 然后,变换会将作物重新缩放为相应参数指定的高度和宽度。 erosion_rate参数控制裁剪后可能丢失原始边界框的面积。 frosting_rate = 0.2表示扩充后的边界框的面积可能比原始边界框的面积小20%。
五、定义增强管道
transform = A.Compose(
[A.RandomSizedBBoxSafeCrop(width=448, height=336, erosion_rate=0.2)],
bbox_params=A.BboxParams(format='coco', label_fields=['category_ids']),
)
六、输入用于增强的图像和边框
我们固定随机种子是为了可视化目的,因此增强将始终产生相同的结果。 在真实的计算机视觉管道中,您不应该在对图像应用转换之前固定随机种子,因为在这种情况下,管道将始终输出相同的图像。 图像增强的目的是每次使用不同的变换。
random.seed(7)
transformed = transform(image=image, bboxes=bboxes, category_ids=category_ids)
visualize(
transformed['image'],
transformed['bboxes'],
transformed['category_ids'],
category_id_to_name,
)
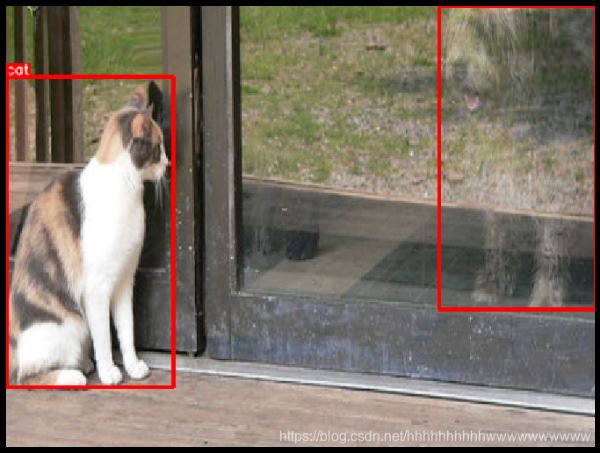
七、其他不同随机种子的示例
random.seed(3)
transformed = transform(image=image, bboxes=bboxes, category_ids=category_ids)
visualize(
transformed['image'],
transformed['bboxes'],
transformed['category_ids'],
category_id_to_name,
)
random.seed(444)
transformed = transform(image=image, bboxes=bboxes, category_ids=category_ids)
visualize(
transformed['image'],
transformed['bboxes'],
transformed['category_ids'],
category_id_to_name,
)

到此这篇关于Python深度学习之使用Albumentations对目标检测任务做增强的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关用Albumentations对目标做增强内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
您可能感兴趣的文章:- python使用matplotlib显示图像失真的解决方案
- Python深度学习之图像标签标注软件labelme详解
- Python深度学习albumentations数据增强库
 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服