1、数值类型
整数:
mysql中的整数类型和pg相比,两者有以下区别:
mysql:mysql中支持int 1,2,3,4,8 字节,同时支持有符号,无符号。并且mysql中支持在数值列中指定zerofill,用来将存储的数值通过填充0的方式达到指定数据类型的长度(mysql8开始不建议使用ZEROFILL属性,并且在将来的MySQL版本中将不再支持该属性)。
pg:pg支持 int 2,4,8 字节,且数值都是有符号的。
mysql整数类型:
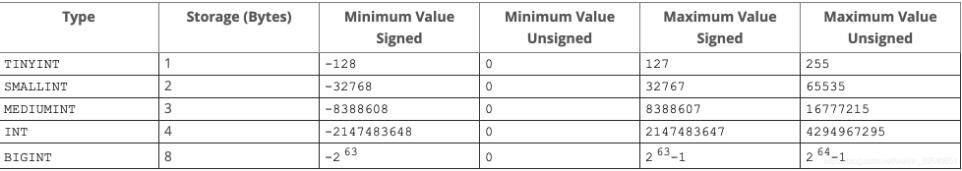
pg整数类型:
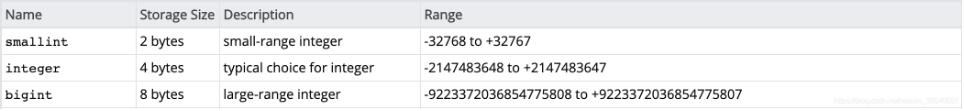
那么对于mysql中的1,3字节整型,或者无符号整型以及zerofill特性,在pg中该如何实现呢?
在pg中我们可以使用domain来实现mysql中的1,3字节整数以及无符号整型。
创建uint8,8字节无符号整型
bill=# create domain uint8 as numeric(20,0) check (value = ((2^64::numeric)::numeric(20,0)-1) and value>=0::numeric(20,0));
CREATE DOMAIN
使用domain,插入整型数据,且大于等于0,小于2^64
bill=# create table t5(c1 uint8);
CREATE TABLE
bill=# insert into t5 values (-1);
ERROR: value for domain uint8 violates check constraint "uint8_check"
bill=# insert into t5 values (0);
INSERT 0 1
bill=# insert into t5 values (18446744073709551615);
INSERT 0 1
bill=# insert into t5 values (18446744073709551616);
ERROR: value for domain uint8 violates check constraint "uint8_check"
bill=# select * from t5;
c1
----------------------
0
18446744073709551615
(2 rows)
同样我们也可以来创建domain实现1,3字节有无符号整型,2,4,8字节无符号等等:
create domain int1 as int2 CHECK (VALUE = 127 AND VALUE >= (-128));
create domain uint1 as int2 CHECK (VALUE = 255 AND VALUE >= 0);
create domain uint2 as int4 CHECK (VALUE = 65535 AND VALUE >= 0);
create domain int3 as int4 CHECK (VALUE = 8388607 AND VALUE >= (-8388608));
create domain uint3 as int4 CHECK (VALUE = 16777215 AND VALUE >= 0);
create domain uint4 as int8 CHECK (VALUE = 4294967295 AND VALUE >= 0);
create domain uint8 as numeric(20,0) check (value = ((2^64::numeric)::numeric(20,0)-1) and value>=0::numeric(20,0));
而对于mysql中的zerofill,我们可以使用lpad函数来实现,并且这也是mysql官方文档中推荐的一种方式。
mysql中zerofill使用方式:
mysql> create table t1(id int1 zerofill);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into t1 values(4);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from t1;
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 004 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
pg中使用lpad函数替代:
bill=# create table t1(id int);
CREATE TABLE
bill=# insert into t1 values (123),(123456);
INSERT 0 2
bill=# select lpad(id::text, greatest(4, length(id::text)), '0'), id from t1;
lpad | id
--------+--------
0123 | 123
123456 | 123456
(2 rows)
numeric类型:
pg和mysql一样都支持decimal,numeric类型来表示浮点数。两者的区别在于:mysql中的numeric类型整数和小数部分均最大支持65digits。
而pg中numeric类型支持的最大范围是:
[左131072,右16383]digits。
例如:
–mysql中
mysql> create table t1(id numeric(66,1));
ERROR 1426 (42000): Too-big precision 66 specified for 'id'. Maximum is 65.
mysql> create table t1(id numeric(65,1));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
–pg中
bill=# create table t4(id numeric(66,1));
CREATE TABLE
浮点类型:
mysql和pg中的浮点数类型基本一致。mysql中4 bytes的浮点数类型有real,float4,4 bytes的浮点数类型double。pg中对应的也有real,float,float4,float8以及double precision,两者基本兼容。
bit类型:
mysql中bit类型一般都是使用整数类型表示,所以支持的bit位数最大只能是64位。而在pg中有专门的bit类型bit(范围1~83886080),以及可变长度的bit类型varbit。
序列:
mysql中创建表时可以使用auto_increment来创建自增列,从而生成一个和该列相关的序列,这个和pg中创建serial类型的列类似,但是两者仍然有明显区别:
mysql:使用auto_increment的自增列必须要建索引,不然会报错。序列的默认初始值是1,步长为1.可以通过修改auto_increment_increment和auto_increment_offset来修改初始值和步长。
pg:pg中创建serial类型的列时会创建相应的序列,支持的数据类型有serial2,serial4,serial8。同时pg创建序列时可以直接指定初始值,步长,maxvalue,cache,circle等参数。其中序列cache预取多个值,可以保证没有性能问题。circle可以指定序列达到最大值后从初始值开始重新计数。
–mysql
mysql> create table t4 (id int auto_increment primary key);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)
–PostgreSQL
bill=# create table t4(id serial);
CREATE TABLE
2、时间类型
mysql:mysql中时间相关的类型有日期date、时间time以及datetime、timestamp和year类型。
pg:pg中的时间数据类型基本和mysql一致。区别在于pg中支持timez类型,即带时区的时间类型,这个mysql中不支持,但是pg中不支持mysql中的year类型,不过我们仍然可以通过创建domain的方式来在pg中实现year类型。
mysql中的year类型表示年份从 1901年到2155。
pg中实现mysql中year类型的方式:
bill=# create domain year as int2 check(value >=1901 and value =2155);
CREATE DOMAIN
bill=# create table ts4(c1 year);
CREATE TABLE
bill=# insert into ts4 values (1000);
ERROR: value for domain year violates check constraint "year_check"
bill=# insert into ts4 values (2019);
INSERT 0 1
bill=# insert into ts4 values (2156);
ERROR: value for domain year violates check constraint "year_check"
3、字符串类型
char/varchar类型:
mysql和pg中都支持char类型来表示固定长度的字符串,varchar类型表示可变长度的字符串类型,两者的区别在于:
mysql:char类型最大255字符,varchar类型最大不超过64字节。
pg:char类型最大10485760字符,varchar类型最大1G字节。同时pg中还支持两种特殊的字符串类型:name类型,固定64字节长度,char类型(即不指定长度),固定1字节长度。
binary/varbinary类型:
mysql中binary(n)最大255个字符,varbinary(n)最大不超过64k字节。使用字节流来存储字符串。而pg中使用bytea类型来表示二进制类型,最大不超过1G字节。
blob/text类型:
mysql中的blob/text类型分别有以下几种:
tinyblob、tinytext 2^8字节
blob、text 2^16字节
mediumblob、mediumtext 2^24字节
longblob、longtext 2^32字节
pg中对应的使用bytea类型和text类型,两者最大长度均为1G字节。
enum类型:
mysql中的枚举类型最大不超过64K个值,而pg中最大为1GB
set类型:
mysql中的集合set类型表示没有重复值的集合,最大64个值,在pg中虽然没有set类型,但是可以通过数组类型去代替,最大支持1GB大小。
4、其它类型
json类型:
mysql和pg中的json类型基本一致,区别在于默写json函数可能稍有区别。不过pg中json类型有2种json和jsonb,不过一般都使用jsonb类型。
除了上面列举的这些类型之外,pg中还支持很多mysql中不支持的数据类型。例如:pg中支持IP地址类型,这个在mysql中常常都是使用int或者varchar之类的数据类型代替。
除此之外还有很多pg内置的数据类型在mysql中是不支持的:货币、interval、平面几何、全文检索、uuid、xml、数组、复合类型、范围类型、域类型等等。
同时pg还有很多外置的数据类型:树类型、多维类型、化学分子、DNA、postgis等等类型。
补充:Oracle与PostgreSQL使用差异对比与总结
JDBC连接:
Oracle的jdbc连接字符串:db.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@192.168.1.1:1521:ORCL
Postgresql的连接字符串:db.url=jdbc:postgresql:@192.168.1.1:5432/database
1、基本数据类型差异
| Oracle |
PostgreSQL |
| Varchar2 |
varchar |
| number |
numeric |
| date |
timestamp/date/time |
| 不支持boolean,可通过0/1代替 |
支持boolean |
| null |
null |
2、基本函数差异
| item |
Oracle |
PostgreSQL |
| 系统当前时间 |
SYSDATE |
now()/CURRENT_TIMESTAMP/CURRENT_DATE/CURRENT_TIME
|
| 对时间或数字截取 |
trunc() |
date_trunc() |
| to_char,to_number, to_date |
自动格式转换 |
需指定日期格式
eg:to_date(timejoin,'yyyy-MM-dd')
|
| 判空操作 |
nvl() |
coalesce() |
| 条件判断 |
decode() |
case...when...then |
| dual伪表 |
支持 |
不支持(查询常量不需要加from) |
其他用法一致的常用函数:
mod(n2,n1) -- n2除n1取余数; sign(n) -- 判断n的符号;
floor(n) -- 取小于等于n的正整数; ceil() -- 取大于等于n的正整数;
round(n,integer) -- 对n四舍五入,保留位数为integer; trunc(n,integer) -- 对n截取,截取保留的位数为integer;
covert(char,dest_sest,source_set) -- 字符集转换,例:convert(username, 'ZHS16GBK','UTF8');
cast(expr as type_name) -- 数据类型转换,常用于数字与字符间转换,例:cast(id_no as varchar);
部分函数的使用简析:
(1)coalesce(COL1,COL2,COL3):返回参数中第一个非null字段值
例如:coalesce(COL1,0):如果COL1为null或‘',则返回默认值0;否则返回COL1的值;
(2)extract(date):对日期特定部分提取(oracle和postgresql使用一致)
例如:
extract(year from now());>>>2018
extract(month from now());>>>9
extract(month from timestamp '2018-09-10 13:59:59');>>>9
(3)对时间截取trunc()和date_trunc()
>>oracle--trunc()的用法:
trunc(sysdate,'yyyy');//返回当前年的第一天>>>2018-01-01
trunc(sysdate, 'mm');//返回当前月的第一天>>>2018-09-01
trunc(sysdate, 'dd');//返回当前时间的年月日>>>2018-09-14
trunc(sysdate, 'hh');//返回当前小时>>>2018-09-14 13:30:50
>>postgreSQL--date_trunc()用法:
date_trunc('year',now());//返回当前时间年的第一天>>>2018-01-01 00:00:00
date_trunc('month',now());//返回当前月的第一天>>2018-09-01 00:00:00
date_trunc('day',now()); //返回当前时间的年月日>>2018-09-14 00:00:00
date_trunc('second',now()); //返回当前时间的年月日时分秒>>2018-09-14 13:30:50
(3)条件判断
Oracle:
Select DECODE (payments_info,'CR','Credit','DB','Debit', null) FROM dual;
PostgreSQL:
Select CASE
WHEN foo = 'CR' THEN 'Credit'
WHEN foo = 'DB' THEN 'Debit'
ELSE 'default'
END
FROM t2;
3、DDL语法差异
oracle和pgSQL操作表结构语法基本一致:
修改表名:alter table tbl_user rename tbl_user2;
添加约束:alter table 表名 add constraint 表名_列名_nn check (is not null)
添加列:alter table tbl_user add age number(3) default 18 not null;
alter table tbl_user add age number(3) default 18 not null after sex;(在指定列后添加列)
删除列:alter table tbl_user drop column age;
修改列:alter table tbl_user modify password default'000000' not null;(修改约束)
修改列名:alter table tbl_user rename column password to pwd;
只有更改列的数据类型写法有些差异
Oracle:ALTER TABLE table_name modify column_name datatype;
PostgreSQL:ALTER TABLE table_name ALTER column_name TYPE datatype;
4、DML语法差异
oracle和pgSQL增删改查语法基本一致,只有upsert有差异
Oracle:有自带的merge into功能(一个强大的操作)

PostgreSQL:不支持merge操作,可以使用on conflict() do
例:
insert into TargetTable
select id,desc
from SourceTable
on conflict (id)
do update set
desc = exclude.desc
5、查询语句差异
(1)查询表中最新n条数据(Oracle有rownum,postgreSQL有limit)
postgreSQL:
select * from olc.olc_member_intebid_info order by create_time desc limit n;
注意:limit必须用于 order by 之后
Oracle:
写法一:
select t.* from (select * from nwd.tc_inte_bid_record order by create_time desc) t where rownum = n;
写法二:
select * from(select t.*, row_number() over(order by create_time desc) rn from nwd.tc_inte_bid_record t) where rn =n;
上述写法一为通用常规写法;写法二可以对分组后数据排序,分组语句写在over()中
(2)子查询
postgresql子查询要求比较严格,必须具有别名才可以
6、 Postgresql命令行常用操作(psql)
psql -d dbname -U username -p 5210 -h 172.0.0.1
--password 'scws123'
如果不想输入密码,可以在.pgpass隐藏文件中添加密码,格式:
172.0.0.1:5210:dbname:username:password
注意.pgpass的权限问题:chmod 0600 ~/.pgpass
-- 查询某个库下的所有表(\dt)
select * from pg_tables where schemaname = 'idn_dw';
-- 查询某个存储过程(\df)
select proname,prosrc from pg_proc where proname = 'func_dwd_customer_info';
-- 查询某个表下的字段(\d tablen_ame)
select table_schema,table_name,t.colname,string_agg(column_name,',') as COLS
from information_schema.columns
LEFT JOIN (select pg_class.relname as tablename,pg_attribute.attname as colname from
pg_constraint inner join pg_class
on pg_constraint.conrelid = pg_class.oid
inner join pg_attribute on pg_attribute.attrelid = pg_class.oid
and pg_attribute.attnum = pg_constraint.conkey[1]
where pg_constraint.contype='p') t
on table_name=t.tablename
where TABLE_NAME = 's10_anfd_rule'
group by table_schema,table_name,t.colname;
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教。
您可能感兴趣的文章:- PostgreSQL实现批量插入、更新与合并操作的方法
- 解决postgresql 数据库 update更新慢的原因
- 将MySQL数据库移植为PostgreSQL
- PostgreSQL使用MySQL外表的步骤详解(mysql_fdw)
- PostgreSQL使用MySQL外表的步骤详解(mysql_fdw)
- 实现MySQL + PostgreSQL批量插入更新insertOrUpdate

 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服