本文将分享15个初学者必看的基础SQL查询语句,都很基础,但是你不一定都会,所以好好看看吧。
1、创建表和数据插入SQL
我们在开始创建数据表和向表中插入演示数据之前,我想给大家解释一下实时数据表的设计理念,这样也许能帮助大家能更好的理解SQL查询。
在数据库设计中,有一条非常重要的规则就是要正确建立主键和外键的关系。
现在我们来创建几个餐厅订单管理的数据表,一共用到3张数据表,Item Master表、Order Master表和Order Detail表。
创建表:
创建Item Master表:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[ItemMasters](
[Item_Code] [varchar](20) NOT NULL,
[Item_Name] [varchar](100) NOT NULL,
[Price] Int NOT NULL,
[TAX1] Int NOT NULL,
[Discount] Int NOT NULL,
[Description] [varchar](200) NOT NULL,
[IN_DATE] [datetime] NOT NULL,
[IN_USR_ID] [varchar](20) NOT NULL,
[UP_DATE] [datetime] NOT NULL,
[UP_USR_ID] [varchar](20) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_ItemMasters] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[Item_Code] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
向Item Master表插入数据:
INSERT INTO [ItemMasters] ([Item_Code],[Item_Name],[Price],[TAX1],[Discount],[Description],[IN_DATE]
,[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE],[UP_USR_ID])
VALUES
('Item001','Coke',55,1,0,'Coke which need to be cold',GETDATE(),'SHANU'
,GETDATE(),'SHANU')
INSERT INTO [ItemMasters] ([Item_Code],[Item_Name],[Price],[TAX1],[Discount],[Description],[IN_DATE]
,[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE],[UP_USR_ID])
VALUES
('Item002','Coffee',40,0,2,'Coffe Might be Hot or Cold user choice',GETDATE(),'SHANU'
,GETDATE(),'SHANU')
INSERT INTO [ItemMasters] ([Item_Code],[Item_Name],[Price],[TAX1],[Discount],[Description],[IN_DATE]
,[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE],[UP_USR_ID])
VALUES
('Item003','Chiken Burger',125,2,5,'Spicy',GETDATE(),'SHANU'
,GETDATE(),'SHANU')
INSERT INTO [ItemMasters] ([Item_Code],[Item_Name],[Price],[TAX1],[Discount],[Description],[IN_DATE]
,[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE],[UP_USR_ID])
VALUES
('Item004','Potato Fry',15,0,0,'No Comments',GETDATE(),'SHANU'
,GETDATE(),'SHANU')
创建Order Master表:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[OrderMasters](
[Order_No] [varchar](20) NOT NULL,
[Table_ID] [varchar](20) NOT NULL,
[Description] [varchar](200) NOT NULL,
[IN_DATE] [datetime] NOT NULL,
[IN_USR_ID] [varchar](20) NOT NULL,
[UP_DATE] [datetime] NOT NULL,
[UP_USR_ID] [varchar](20) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_OrderMasters] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[Order_No] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
向Order Master表插入数据:
INSERT INTO [OrderMasters]
([Order_No],[Table_ID] ,[Description],[IN_DATE],[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE],[UP_USR_ID])
VALUES
('Ord_001','T1','',GETDATE(),'SHANU' ,GETDATE(),'SHANU')
INSERT INTO [OrderMasters]
([Order_No],[Table_ID] ,[Description],[IN_DATE],[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE],[UP_USR_ID])
VALUES
('Ord_002','T2','',GETDATE(),'Mak' ,GETDATE(),'MAK')
INSERT INTO [OrderMasters]
([Order_No],[Table_ID] ,[Description],[IN_DATE],[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE],[UP_USR_ID])
VALUES
('Ord_003','T3','',GETDATE(),'RAJ' ,GETDATE(),'RAJ')
创建Order Detail表:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[OrderDetails](
[Order_Detail_No] [varchar](20) NOT NULL,
[Order_No] [varchar](20) CONSTRAINT fk_OrderMasters FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES OrderMasters(Order_No),
[Item_Code] [varchar](20) CONSTRAINT fk_ItemMasters FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES ItemMasters(Item_Code),
[Notes] [varchar](200) NOT NULL,
[QTY] INT NOT NULL,
[IN_DATE] [datetime] NOT NULL,
[IN_USR_ID] [varchar](20) NOT NULL,
[UP_DATE] [datetime] NOT NULL,
[UP_USR_ID] [varchar](20) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_OrderDetails] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[Order_Detail_No] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
--Now letrsquo;s insert the 3 items for the above Order No 'Ord_001'.
INSERT INTO [OrderDetails]
([Order_Detail_No],[Order_No],[Item_Code],[Notes],[QTY]
,[IN_DATE],[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE],[UP_USR_ID])
VALUES
('OR_Dt_001','Ord_001','Item001','Need very Cold',3
,GETDATE(),'SHANU' ,GETDATE(),'SHANU')
INSERT INTO [OrderDetails]
([Order_Detail_No],[Order_No],[Item_Code],[Notes],[QTY]
,[IN_DATE],[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE],[UP_USR_ID])
VALUES
('OR_Dt_002','Ord_001','Item004','very Hot ',2
,GETDATE(),'SHANU' ,GETDATE(),'SHANU')
INSERT INTO [OrderDetails]
([Order_Detail_No],[Order_No],[Item_Code],[Notes],[QTY]
,[IN_DATE],[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE],[UP_USR_ID])
VALUES
('OR_Dt_003','Ord_001','Item003','Very Spicy',4
,GETDATE(),'SHANU' ,GETDATE(),'SHANU')
向Order Detail表插入数据:
INSERT INTO [OrderDetails]
([Order_Detail_No],[Order_No],[Item_Code],[Notes],[QTY]
,[IN_DATE],[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE],[UP_USR_ID])
VALUES
('OR_Dt_004','Ord_002','Item002','Need very Hot',2
,GETDATE(),'SHANU' ,GETDATE(),'SHANU')
INSERT INTO [OrderDetails]
([Order_Detail_No],[Order_No],[Item_Code],[Notes],[QTY]
,[IN_DATE],[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE],[UP_USR_ID])
VALUES
('OR_Dt_005','Ord_002','Item003','very Hot ',2
,GETDATE(),'SHANU' ,GETDATE(),'SHANU')
INSERT INTO [OrderDetails]
([Order_Detail_No],[Order_No],[Item_Code],[Notes],[QTY]
,[IN_DATE],[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE],[UP_USR_ID])
VALUES
('OR_Dt_006','Ord_003','Item003','Very Spicy',4
,GETDATE(),'SHANU' ,GETDATE(),'SHANU')
2、简单的Select查询语句
Select查询语句是SQL中最基本也是最重要的DML语句之一。那么什么是DML?DML全称Data Manipulation Language(数据操纵语言命令),它可以使用户能够查询数据库以及操作已有数据库中的数据。
下面我们在SQL Server中用select语句来查询我的姓名(Name):
SELECT 'My Name Is SYED SHANU'
-- With Column Name using 'AS'
SELECT 'My Name Is SYED SHANU' as 'MY NAME'
-- With more then the one Column
SELECT 'My Name' as 'Column1', 'Is' as 'Column2', 'SYED SHANU' as 'Column3'
在数据表中使用select查询:
-- To Display all the columns from the table we use * operator in select Statement.
Select * from ItemMasters
-- If we need to select only few fields from a table we can use the Column Name in Select Statement.
Select Item_Code
,Item_name as Item
,Price
,Description
,In_DATE
FROM
ItemMasters
3、合计和标量函数
合计函数和标量函数都是SQL Server的内置函数,我们可以在select查询语句中使用它们,比如Count(), Max(), Sum(), Upper(), lower(), Round()等等。下面我们用SQL代码来解释这些函数的用法:
select * from ItemMasters
-- Aggregate
-- COUNT() -> returns the Total no of records from table , AVG() returns the Average Value from Colum,MAX() Returns MaX Value from Column
-- ,MIN() returns Min Value from Column,SUM() sum of total from Column
Select Count(*) TotalRows,AVG(Price) AVGPrice
,MAX(Price) MAXPrice,MIN(Price) MinPrice,Sum(price) PriceTotal
FROM ItemMasters
-- Scalar
-- UCASE() -> Convert to Upper Case ,LCASE() -> Convert to Lower Case,
-- SUBSTRING() ->Display selected char from column ->SUBSTRING(ColumnName,StartIndex,LenthofChartoDisplay)
--,LEN() -> lenth of column date,
-- ROUND() -> Which will round the value
SELECT UPPER(Item_NAME) Uppers,LOWER(Item_NAME) Lowers,
SUBSTRING(Item_NAME,2,3) MidValue,LEN(Item_NAME) Lenths
,SUBSTRING(Item_NAME,2,LEN(Item_NAME)) MidValuewithLenFunction,
ROUND(Price,0) as Rounded
FROM ItemMasters
4、日期函数
在我们的项目数据表中基本都会使用到日期列,因此日期函数在项目中扮演着非常重要的角色。有时候我们对日期函数要非常的小心,它随时可以给你带来巨大的麻烦。在项目中,我们要选择合适的日期函数和日期格式,下面是一些SQL日期函数的例子:
-- GETDATE() -> to Display the Current Date and Time
-- Format() -> used to display our date in our requested format
Select GETDATE() CurrentDateTime, FORMAT(GETDATE(),'yyyy-MM-dd') AS DateFormats,
FORMAT(GETDATE(),'HH-mm-ss')TimeFormats,
CONVERT(VARCHAR(10),GETDATE(),10) Converts1,
CONVERT(VARCHAR(24),GETDATE(),113),
CONVERT(NVARCHAR, getdate(), 106) Converts2 ,-- here we used Convert Function
REPLACE(convert(NVARCHAR, getdate(), 106), ' ', '/') Formats-- Here we used replace and --convert functions.
--first we convert the date to nvarchar and then we replace the '' with '/'
select * from Itemmasters
Select ITEM_NAME,IN_DATE CurrentDateTime, FORMAT(IN_DATE,'yyyy-MM-dd') AS DateFormats,
FORMAT(IN_DATE,'HH-mm-ss')TimeFormats,
CONVERT(VARCHAR(10),IN_DATE,10) Converts1,
CONVERT(VARCHAR(24),IN_DATE,113),
convert(NVARCHAR, IN_DATE, 106) Converts2 ,-- here we used Convert Function
REPLACE(convert(NVARCHAR,IN_DATE, 106), ' ', '/') Formats
FROM Itemmasters
DatePart –> 该函数可以获取年、月、日的信息。
DateADD –> 该函数可以对当前的日期进行加减。
DateDiff –> 该函数可以比较2个日期。
--Datepart DATEPART(dateparttype,yourDate)
SELECT DATEPART(yyyy,getdate()) AS YEARs ,
DATEPART(mm,getdate()) AS MONTHS,
DATEPART(dd,getdate()) AS Days,
DATEPART(week,getdate()) AS weeks,
DATEPART(hour,getdate()) AS hours
--Days Add to add or subdtract date from a selected date.
SELECT GetDate()CurrentDate,DATEADD(day,12,getdate()) AS AddDays ,
DATEADD(day,-4,getdate()) AS FourDaysBeforeDate
-- DATEDIFF() -> to display the Days between 2 dates
select DATEDIFF(year,'2003-08-05',getdate()) yearDifferance ,
DATEDIFF(day,DATEADD(day,-24,getdate()),getdate()) daysDifferent,
DATEDIFF(month,getdate(),DATEADD(Month,6,getdate())) MonthDifferance
5、其他Select函数
Top —— 结合select语句,Top函数可以查询头几条和末几条的数据记录。
Order By —— 结合select语句,Order By可以让查询结果按某个字段正序和逆序输出数据记录。
--Top to Select Top first and last records using Select Statement.
Select * FROM ItemMasters
--> First Display top 2 Records
Select TOP 2 Item_Code
,Item_name as Item
,Price
,Description
,In_DATE
FROM ItemMasters
--> to Display the Last to Records we need to use the Order By Clause
-- order By to display Records in assending or desending order by the columns
Select TOP 2 Item_Code
,Item_name as Item
,Price
,Description
,In_DATE
FROM ItemMasters
ORDER BY Item_Code DESC
Distinct —— distinct关键字可以过滤重复的数据记录。
Select * FROM ItemMasters
--Distinct -> To avoid the Duplicate records we use the distinct in select statement
-- for example in this table we can see here we have the duplicate record 'Chiken Burger'
-- but with different Item_Code when i use the below select statement see what happen
Select Item_name as Item
,Price
,Description
,IN_USR_ID
FROM ItemMasters
-- here we can see the Row No 3 and 5 have the duplicate record to avoid this we use the distinct Keyword in select statement.
select Distinct Item_name as Item
,Price
,Description
,IN_USR_ID
FROM ItemMasters
6、Where子句
Where子句在SQL Select查询语句中非常重要,为什么要使用where子句?什么时候使用where子句?where子句是利用一些条件来过滤数据结果集。
下面我们从10000条数据记录中查询Order_No为某个值或者某个区间的数据记录,另外还有其他的条件。
Select * from ItemMasters
Select * from OrderDetails
--Where -> To display the data with certain conditions
-- Now below example which will display all the records which has Item_Name='Coke'
select * FROM ItemMasters WHERE ITEM_NAME='COKE'
-- If we want display all the records Iten_Name which Starts with 'C' then we use Like in where clause.
SELECT * FROM ItemMasters WHERE ITEM_NAME Like 'C%'
--> here we display the ItemMasters where the price will be greater then or equal to 40.
--> to use more then one condition we can Use And or Or operator.
--If we want to check the data between to date range then we can use Between Operator in Where Clause.
select Item_name as Item
,Price
,Description
,IN_USR_ID
FROM ItemMasters
WHERE
ITEM_NAME Like 'C%'
AND
price >=40
--> here we display the OrderDetails where the Qty will be greater 3
Select * FROM OrderDetails WHERE qty>3
Where – In 子句
-- In clause -> used to display the data which is in the condition
select *
FROM ItemMasters
WHERE
Item_name IN ('Coffee','Chiken Burger')
-- In clause with Order By - Here we display the in descending order.
select *
FROM ItemMasters
WHERE
Item_name IN ('Coffee','Chiken Burger')
ORDER BY Item_Code Desc
Where – Between子句
-- between -> Now if we want to display the data between to date range then we use betweeen keyword
select * FROM ItemMasters
select * FROM ItemMasters
WHERE
In_Date BETWEEN '2014-09-22 15:59:02.853' AND '2014-09-22 15:59:02.853'
select * FROM ItemMasters
WHERE
ITEM_NAME Like 'C%'
AND
In_Date BETWEEN '2014-09-22 15:59:02.853' AND '2014-09-22 15:59:02.853'
查询某个条件区间的数据,我们常常使用between子句。
7、Group By 子句
Group By子句可以对查询的结果集按指定字段分组:
--Group By -> To display the data with group result.Here we can see we display all the AQggregate result by Item Name
Select ITEM_NAME,Count(*) TotalRows,AVG(Price) AVGPrice
,MAX(Price) MAXPrice,MIN(Price) MinPrice,Sum(price) PriceTotal
FROM
ItemMasters
GROUP BY ITEM_NAME
-- Here this group by will combine all the same Order_No result and make the total or each order_NO
Select Order_NO,Sum(QTy) as TotalQTY
FROM OrderDetails
where qty>=2
GROUP BY Order_NO
-- Here the Total will be created by order_No and Item_Code
Select Order_NO,Item_Code,Sum(QTy) as TotalQTY
FROM OrderDetails
where qty>=2
GROUP BY Order_NO,Item_Code
Order By Order_NO Desc,Item_Code
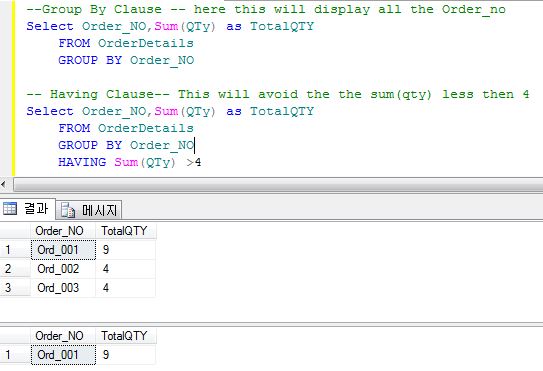
Group By Having 子句
--Group By Clause -- here this will display all the Order_no
Select Order_NO,Sum(QTy) as TotalQTY
FROM OrderDetails
GROUP BY Order_NO
-- Having Clause-- This will avoid the the sum(qty) less then 4
Select Order_NO,Sum(QTy) as TotalQTY
FROM OrderDetails
GROUP BY Order_NO
HAVING Sum(QTy) >4
8、子查询
子查询一般出现在where内连接查询和嵌套查询中,select、update和delete语句中均可以使用。
--Sub Query -- Here we used the Sub query in where clause to get all the Item_Code where the price>40 now this sub
--query reslut we used in our main query to filter all the records which Item_code from Subquery result
SELECT * FROM ItemMasters
WHERE Item_Code IN
(SELECT Item_Code FROM ItemMasters WHERE price > 40)
-- Sub Query with Insert Statement
INSERT INTO ItemMasters ([Item_Code] ,[Item_Name],[Price],[TAX1],[Discount],[Description],[IN_DATE]
,[IN_USR_ID],[UP_DATE] ,[UP_USR_ID])
Select 'Item006'
,Item_Name,Price+4,TAX1,Discount,Description
,GetDate(),'SHANU',GetDate(),'SHANU'
from ItemMasters
where Item_code='Item002'
--After insert we can see the result as
Select * from ItemMasters
9、连接查询
到目前为止我们接触了不少单表的查询语句,现在我们来使用连接查询获取多个表的数据。
简单的join语句:
--Now we have used the simple join with out any condition this will display all the
-- records with duplicate data to avaoid this we see our next example with condition
SELECT * FROM Ordermasters,OrderDetails
-- Simple Join with Condition now here we can see the duplicate records now has been avoided by using the where checing with both table primaryKey field
SELECT *
FROM
Ordermasters as M, OrderDetails as D
where M.Order_NO=D.Order_NO
and M.Order_NO='Ord_001'
-- Now to make more better understanding we need to select the need fields from both
--table insted of displaying all column.
SELECT M.order_NO,M.Table_ID,D.Order_detail_no,Item_code,Notes,Qty
FROM
Ordermasters as M, OrderDetails as D
where M.Order_NO=D.Order_NO
-- Now lets Join 3 table
SELECT M.order_NO,M.Table_ID,D.Order_detail_no,I.Item_Name,D.Notes,D.Qty,I.Price,
I.Price*D.Qty as TotalPrice
FROM
Ordermasters as M, OrderDetails as D,ItemMasters as I
where
M.Order_NO=D.Order_NO AND D.Item_Code=I.Item_Code
Inner Join,Left Outer Join,Right Outer Join and Full outer Join
下面是各种类型的连接查询代码:
--INNER JOIN
--This will display the records which in both table Satisfy here i have used Like in where class which display the
SELECT M.order_NO,M.Table_ID,D.Order_detail_no,I.Item_Name,D.Notes,D.Qty,I.Price,I.Price*D.Qty as TotalPrice
FROM
Ordermasters as M Inner JOIN OrderDetails as D
ON M.Order_NO=D.Order_NO
INNER JOIN ItemMasters as I
ON D.Item_Code=I.Item_Code
WHERE
M.Table_ID like 'T%'
--LEFT OUTER JOIN
--This will display the records which Left side table Satisfy
SELECT M.order_NO,M.Table_ID,D.Order_detail_no,I.Item_Name,D.Notes,D.Qty,I.Price,I.Price*D.Qty as TotalPrice
FROM
Ordermasters as M LEFT OUTER JOIN OrderDetails as D
ON M.Order_NO=D.Order_NO
LEFT OUTER JOIN ItemMasters as I
ON D.Item_Code=I.Item_Code
WHERE
M.Table_ID like 'T%'
--RIGHT OUTER JOIN
--This will display the records which Left side table Satisfy
SELECT M.order_NO,M.Table_ID,D.Order_detail_no,I.Item_Name,D.Notes,D.Qty,I.Price,I.Price*D.Qty as TotalPrice
FROM
Ordermasters as M RIGHT OUTER JOIN OrderDetails as D
ON M.Order_NO=D.Order_NO
RIGHT OUTER JOIN ItemMasters as I
ON D.Item_Code=I.Item_Code
WHERE
M.Table_ID like 'T%'
--FULL OUTER JOIN
--This will display the records which Left side table Satisfy
SELECT M.order_NO,M.Table_ID,D.Order_detail_no,I.Item_Name,D.Notes,D.Qty,I.Price,I.Price*D.Qty as TotalPrice
FROM
Ordermasters as M FULL OUTER JOIN OrderDetails as D
ON M.Order_NO=D.Order_NO
FULL OUTER JOIN ItemMasters as I
ON D.Item_Code=I.Item_Code
WHERE
M.Table_ID like 'T%'
10、Union合并查询
Union查询可以把多张表的数据合并起来,Union只会把唯一的数据查询出来,而Union ALL则会把重复的数据也查询出来。
Select column1,Colum2 from Table1
Union
Select Column1,Column2 from Table2
Select column1,Colum2 from Table1
Union All
Select Column1,Column2 from Table2
具体的例子如下:
--Select with different where condition which display the result as 2 Table result
select Item_Code,Item_Name,Price,Description FROM ItemMasters where price =44
select Item_Code,Item_Name,Price,Description FROM ItemMasters where price >44
-- Union with same table but with different where condition now which result as one table which combine both the result.
select Item_Code,Item_Name,Price,Description FROM ItemMasters where price =44
UNION
select Item_Code,Item_Name,Price,Description FROM ItemMasters where price >44
-- Union ALL with Join sample
SELECT M.order_NO,M.Table_ID,D.Order_detail_no,I.Item_Name,D.Notes,D.Qty,I.Price,I.Price*D.Qty as TotalPrice
FROM
Ordermasters as M (NOLOCK) Inner JOIN OrderDetails as D
ON M.Order_NO=D.Order_NO INNER JOIN ItemMasters as I
ON D.Item_Code=I.Item_Code WHERE I.Price =44
Union ALL
SELECT M.order_NO,M.Table_ID,D.Order_detail_no,I.Item_Name,D.Notes,D.Qty,I.Price,I.Price*D.Qty as TotalPrice
FROM
Ordermasters as M (NOLOCK) Inner JOIN OrderDetails as D
ON M.Order_NO=D.Order_NO INNER JOIN ItemMasters as I
ON D.Item_Code=I.Item_Code WHERE I.Price>44
11、公用表表达式(CTE)——With语句
CTE可以看作是一个临时的结果集,可以在接下来的一个SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE,MERGE语句中被多次引用。使用公用表达式可以让语句更加清晰简练。
declare @sDate datetime,
@eDate datetime;
select @sDate = getdate()-5,
@eDate = getdate()+16;
--select @sDate StartDate,@eDate EndDate
;with cte as
(
select @sDate StartDate,'W'+convert(varchar(2),
DATEPART( wk, @sDate))+'('+convert(varchar(2),@sDate,106)+')' as 'SDT'
union all
select dateadd(DAY, 1, StartDate) ,
'W'+convert(varchar(2),DATEPART( wk, StartDate))+'('+convert(varchar(2),
dateadd(DAY, 1, StartDate),106)+')' as 'SDT'
FROM cte
WHERE dateadd(DAY, 1, StartDate)= @eDate
)
select * from cte
option (maxrecursion 0)
12、视图
很多人对视图View感到很沮丧,因为它看起来跟select语句没什么区别。在视图中我们同样可以使用select查询语句,但是视图对我们来说依然非常重要。
假设我们要联合查询4张表中的20几个字段,那么这个select查询语句会非常复杂。但是这样的语句我们在很多地方都需要用到,如果将它编写成视图,那么使用起来会方便很多。利用视图查询有以下几个优点:
- 一定程度上提高查询速度
- 可以对一些字段根据不同的权限进行屏蔽,因此提高了安全性
- 对多表的连接查询会非常方便
下面是一个视图的代码例子:
CREATE
VIEW viewname
AS
Select ColumNames from yourTable
Example :
-- Here we create view for our Union ALL example
Create
VIEW myUnionVIEW
AS
SELECT M.order_NO,M.Table_ID,D.Order_detail_no,I.Item_Name,D.Notes,D.Qty,I.Price,
I.Price*D.Qty as TotalPrice
FROM
Ordermasters as M Inner JOIN OrderDetails as D
ON M.Order_NO=D.Order_NO INNER JOIN ItemMasters as I
ON D.Item_Code=I.Item_Code WHERE I.Price =44
Union ALL
SELECT M.order_NO,M.Table_ID,D.Order_detail_no,I.Item_Name,D.Notes,D.Qty,I.Price,
I.Price*D.Qty as TotalPrice
FROM
Ordermasters as M Inner JOIN OrderDetails as D
ON M.Order_NO=D.Order_NO INNER JOIN ItemMasters as I
ON D.Item_Code=I.Item_Code WHERE I.Price>44
-- View Select query
Select * from myUnionVIEW
-- We can also use the View to display with where condition and with selected fields
Select order_Detail_NO,Table_ID,Item_Name,Price from myUnionVIEW where price >40
13、Pivot行转列
Pivot可以帮助你实现数据行转换成数据列,具体用法如下:
-- Simple Pivot Example
SELECT * FROM ItemMasters
PIVOT(SUM(Price)
FOR ITEM_NAME IN ([Chiken Burger], Coffee,Coke)) AS PVTTable
-- Pivot with detail example
SELECT *
FROM (
SELECT
ITEM_NAME,
price as TotAmount
FROM ItemMasters
) as s
PIVOT
(
SUM(TotAmount)
FOR [ITEM_NAME] IN ([Chiken Burger], [Coffee],[Coke])
)AS MyPivot
14、存储过程
我经常看到有人提问如何在SQL Server中编写多条查询的SQL语句,然后将它们使用到C#程序中去。存储过程就可以完成这样的功能,存储过程可以将多个SQL查询聚集在一起,创建存储过程的基本结构是这样的:
CREATE PROCEDURE [ProcedureName]
AS
BEGIN
-- Select or Update or Insert query.
END
To execute SP we use
exec ProcedureName
创建一个没有参数的存储过程:
-- =============================================
-- Author : Shanu
-- Create date : 2014-09-15
-- Description : To Display Pivot Data
-- Latest
-- Modifier : Shanu
-- Modify date : 2014-09-15
-- =============================================
-- exec USP_SelectPivot
-- =============================================
Create PROCEDURE [dbo].[USP_SelectPivot]
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @MyColumns AS NVARCHAR(MAX),
@SQLquery AS NVARCHAR(MAX)
-- here first we get all the ItemName which should be display in Columns we use this in our necxt pivot query
select @MyColumns = STUFF((SELECT ',' + QUOTENAME(Item_NAME)
FROM ItemMasters
GROUP BY Item_NAME
ORDER BY Item_NAME
FOR XML PATH(''), TYPE
).value('.', 'NVARCHAR(MAX)')
,1,1,'')
-- here we use the above all Item name to disoplay its price as column and row display
set @SQLquery = N'SELECT ' + @MyColumns + N' from
(
SELECT
ITEM_NAME,
price as TotAmount
FROM ItemMasters
) x
pivot
(
SUM(TotAmount)
for ITEM_NAME in (' + @MyColumns + N')
) p '
exec sp_executesql @SQLquery;
RETURN
END
15、函数Function
之前我们介绍了MAX(),SUM(), GetDate()等最基本的SQL函数,现在我们来看看如何创建自定义SQL函数。创建函数的格式如下:
Create Function functionName
As
Begin
END
下面是一个简单的函数示例:
Alter FUNCTION [dbo].[ufnSelectitemMaster]()
RETURNS int
AS
-- Returns total Row count of Item Master.
BEGIN
DECLARE @RowsCount AS int;
Select @RowsCount= count(*)+1 from ItemMasters
RETURN @RowsCount;
END
-- to View Function we use select and fucntion Name
select [dbo].[ufnSelectitemMaster]()
下面的一个函数可以实现从给定的日期中得到当前月的最后一天:
ALTER FUNCTION [dbo].[ufn_LastDayOfMonth]
(
@DATE NVARCHAR(10)
)
RETURNS NVARCHAR(10)
AS
BEGIN
RETURN CONVERT(NVARCHAR(10), DATEADD(D, -1, DATEADD(M, 1, CAST(SUBSTRING(@DATE,1,7) + '-01' AS DATETIME))), 120)
END
SELECT dbo.ufn_LastDayOfMonth('2014-09-01')AS LastDay
以上就是适合初学者学习的基础SQL查询语句,希望对大家学习SQL查询语句有所帮助。
您可能感兴趣的文章:- SQL查询语句精华使用简要
- SQl 跨服务器查询语句
- SQL查询语句通配符与ACCESS模糊查询like的解决方法
- SQL Server SQL高级查询语句小结
- T-SQL 查询语句的执行顺序解析
- 基于SQL中的数据查询语句汇总
- oracle常用sql查询语句部分集合(图文)
- MySql日期查询语句详解
- mysql分页原理和高效率的mysql分页查询语句
- Android中的SQL查询语句LIKE绑定参数问题解决办法(sqlite数据库)
 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服