今天用go实现一个简单的负载均衡的算法,虽然简单,还是要写一下。
1.首先就是服务器的信息
package balance
type Instance struct {
host string
port int
}
func NewInstance(host string, port int) *Instance {
return Instance{
host: host,
port: port,
}
}
func (p *Instance) GetHost() string {
return p.host
}
func (p *Instance) GetPort() int {
return p.port
}
2.接着定义接口
package balance
type Balance interface {
/**
*负载均衡算法
*/
DoBalance([] *Instance,...string) (*Instance,error)
}
3.接着,是实现接口,random.go
package balance
import (
"errors"
"math/rand"
)
func init() {
RegisterBalance("random",RandomBalance{})
}
type RandomBalance struct {
}
func (p *RandomBalance) DoBalance(insts [] *Instance,key...string) (inst *Instance, err error) {
if len(insts) == 0 {
err = errors.New("no instance")
return
}
lens := len(insts)
index := rand.Intn(lens)
inst = insts[index]
return
}
roundrobin.go
package balance
import (
"errors"
)
func init() {
RegisterBalance("round", RoundRobinBalance{})
}
type RoundRobinBalance struct {
curIndex int
}
func (p *RoundRobinBalance) DoBalance(insts [] *Instance, key ...string) (inst *Instance, err error) {
if len(insts) == 0 {
err = errors.New("no instance")
return
}
lens := len(insts)
if p.curIndex >= lens {
p.curIndex = 0
}
inst = insts[p.curIndex]
p.curIndex++
return
}
4 然后,全部交给管理器来管理,这也是为什么上面的文件全部重写了init函数
package balance
import (
"fmt"
)
type BalanceMgr struct {
allBalance map[string]Balance
}
var mgr = BalanceMgr{
allBalance: make(map[string]Balance),
}
func (p *BalanceMgr) registerBalance(name string, b Balance) {
p.allBalance[name] = b
}
func RegisterBalance(name string, b Balance) {
mgr.registerBalance(name, b)
}
func DoBalance(name string, insts []*Instance) (inst *Instance, err error) {
balance, ok := mgr.allBalance[name]
if !ok {
err = fmt.Errorf("not fount %s", name)
fmt.Println("not found ",name)
return
}
inst, err = balance.DoBalance(insts)
if err != nil {
err = fmt.Errorf(" %s erros", name)
return
}
return
}
下面进行测试:
func main() {
var insts []*balance.Instance
for i := 0; i 10; i++ {
host := fmt.Sprintf("192.168.%d.%d", rand.Intn(255), rand.Intn(255))
port, _ := strconv.Atoi(fmt.Sprintf("880%d", i))
one := balance.NewInstance(host, port)
insts = append(insts, one)
}
var name = "round"
if len(os.Args) > 1 {
name = os.Args[1]
}
for {
inst, err := balance.DoBalance(name, insts)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("do balance err")
time.Sleep(time.Second)
continue
}
fmt.Println(inst)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
}
5.如果想扩展这个,又不入侵原来的代码结构,可以类比上面实现dobalance接口即可
package add
import (
"awesomeProject/test/balance"
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"hash/crc32"
)
func init() {
balance.RegisterBalance("hash", HashBalance{})
}
type HashBalance struct {
key string
}
func (p *HashBalance) DoBalance(insts [] *balance.Instance, key ...string) (inst *balance.Instance, err error) {
defKey := fmt.Sprintf("%d", rand.Int())
if len(key) > 0 {
defKey = key[0]
}
lens := len(insts)
if lens == 0 {
err = fmt.Errorf("no balance")
return
}
hashVal := crc32.Checksum([]byte(defKey), crc32.MakeTable(crc32.IEEE))
index := int(hashVal) % lens
inst = insts[index]
return
}
这样就能交给管理器统一管理了,而且不会影响原来的api。
补充:golang grpc配合nginx实现负载均衡
概述
grpc负载均衡有主要有进程内balance, 进程外balance, proxy 三种方式,本文叙述的是proxy方式,以前进程内的方式比较流行,靠etcd或者consul等服务发现来轮询,随机等方式实现负载均衡。
现在nginx 1.13过后正式支持grpc, 由于nginx稳定,高并发量,功能强大,更难能可贵的是部署方便,并且不像进程内balance那样不同的语言要写不同的实现,因此我非常推崇这种方式。
nginx的配置
确认安装版本大于1.13的nginx后打开配置文件,写入如下配置
upstream lb{
#负载均衡的grpc服务器地址
server 127.0.0.1:50052;
server 127.0.0.1:50053;
server 127.0.0.1:50054;
#keepalive 500;#这个东西是nginx和rpc服务器群保持长连接的总数,设置可以提高效率,同时避免nginx到rpc服务器之间默认是短连接并发过后造成time_wait过多
}
server {
listen 9527 http2;
access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main;
http2_max_requests 10000;#这里默认是1000,并发量上来会报错,因此设置大一点
#grpc_socket_keepalive on;#这个东西nginx1.5过后支持
location / {
grpc_pass grpc://lb;
error_page 502 = /error502grpc;
}
location = /error502grpc {
internal;
default_type application/grpc;
add_header grpc-status 14;
add_header grpc-message "Unavailable";
return 204;
}
}
可以在host.access.log日志文件里面看到数据转发记录
proto文件:
syntax = "proto3"; // 指定proto版本
package grpctest; // 指定包名
// 定义Hello服务
service Hello {
// 定义SayHello方法
rpc SayHello(HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
}
// HelloRequest 请求结构
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
// HelloReply 响应结构
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}
客户端:
客户端连接地址填写nginx的监听地址,相关代码如下:
package main
import (
pb "protobuf/grpctest" // 引入proto包
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"google.golang.org/grpc/grpclog"
"fmt"
"time"
)
const (
// Address gRPC服务地址
Address = "127.0.0.1:9527"
)
func main() {
// 连接
conn, err := grpc.Dial(Address, grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
grpclog.Fatalln(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
// 初始化客户端
c := pb.NewHelloClient(conn)
reqBody := new(pb.HelloRequest)
reqBody.Name = "gRPC"
// 调用方法
for{
r, err := c.SayHello(context.Background(), reqBody)
if err != nil {
grpclog.Fatalln(err)
}
fmt.Println(r.Message)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
}
服务端:
package main
import (
"net"
"fmt"
pb "protobuf/grpctest" // 引入编译生成的包
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"google.golang.org/grpc/grpclog"
)
const (
// Address gRPC服务地址
Address = "127.0.0.1:50052"
//Address = "127.0.0.1:50053"
//Address = "127.0.0.1:50054"
)
var HelloService = helloService{}
type helloService struct{}
func (this helloService) SayHello(ctx context.Context,in *pb.HelloRequest)(*pb.HelloReply,error){
resp := new(pb.HelloReply)
resp.Message = Address+" hello"+in.Name+"."
return resp,nil
}
func main(){
listen,err:=net.Listen("tcp",Address)
if err != nil{
grpclog.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
s:=grpc.NewServer()
pb.RegisterHelloServer(s,HelloService)
grpclog.Println("Listen on " + Address)
s.Serve(listen)
}
测试
以50052,50053,50054 3个端口启3个服务端进程,运行客户端代码,即可看见如下效果:
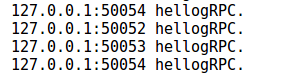
负载均衡完美实现, 打开日志文件,可以看到post的地址为 /grpctest.Hello/SayHello,nginx配置为所有请求都按默认 localtion / 转发,因此 nginx再配上合适的路由规则,还可实现更灵活转发,也可达到微服务注册的目的,非常方便。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教。
您可能感兴趣的文章:- Golang 实现简单随机负载均衡
- golang grpc 负载均衡的方法
- Django高并发负载均衡实现原理详解
- Golang实现四种负载均衡的算法(随机,轮询等)
 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服