一、所需工具
**Python版本:**3.5.4(64bit)
二、相关模块
- opencv_python模块
- sklearn模块
- numpy模块
- dlib模块
- 一些Python自带的模块。
三、环境搭建
(1)安装相应版本的Python并添加到环境变量中;
(2)pip安装相关模块中提到的模块。
例如:
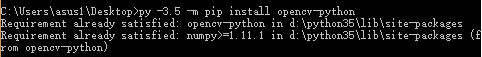
若pip安装报错,请自行到:
http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/
下载pip安装报错模块的whl文件,并使用:
pip install whl文件路径+whl文件名安装。
例如:
(已在相关文件中提供了编译好的用于dlib库安装的whl文件——>因为这个库最不好装)

参考文献链接
【1】xxxPh.D.的博客
http://www.learnopencv.com/computer-vision-for-predicting-facial-attractiveness/
【2】华南理工大学某实验室
http://www.hcii-lab.net/data/SCUT-FBP/EN/introduce.html
四、主要思路
(1)模型训练
用了PCA算法对特征进行了压缩降维;
然后用随机森林训练模型。
数据源于网络,据说数据“发源地”就是华南理工大学某实验室,因此我在参考文献上才加上了这个实验室的链接。
(2)提取人脸关键点
主要使用了dlib库。
使用官方提供的模型构建特征提取器。
(3)特征生成
完全参考了xxxPh.D.的博客。
(4)颜值预测
利用之前的数据和模型进行颜值预测。
使用方式
有特殊疾病者请慎重尝试预测自己的颜值,本人不对颜值预测的结果和带来的所有负面影响负责!!!
言归正传。
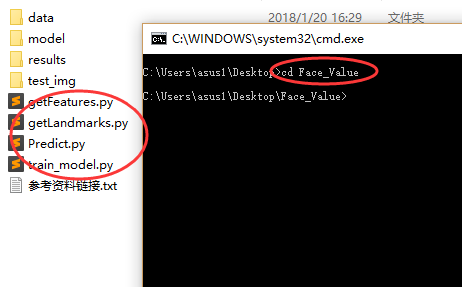
环境搭建完成后,解压相关文件中的Face_Value.rar文件,cmd窗口切换到解压后的*.py文件所在目录。
例如:
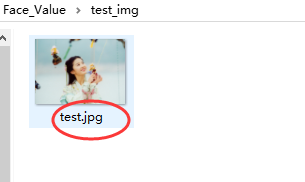
打开test_img文件夹,将需要预测颜值的照片放入并重命名为test.jpg。
例如:
若嫌麻烦或者有其他需求,请自行修改:
getLandmarks.py文件中第13行。
最后依次运行:
train_model.py(想直接用我模型的请忽略此步)
# 模型训练脚本
import numpy as np
from sklearn import decomposition
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.externals import joblib
# 特征和对应的分数路径
features_path = './data/features_ALL.txt'
ratings_path = './data/ratings.txt'
# 载入数据
# 共500组数据
# 其中前480组数据作为训练集,后20组数据作为测试集
features = np.loadtxt(features_path, delimiter=',')
features_train = features[0: -20]
features_test = features[-20: ]
ratings = np.loadtxt(ratings_path, delimiter=',')
ratings_train = ratings[0: -20]
ratings_test = ratings[-20: ]
# 训练模型
# 这里用PCA算法对特征进行了压缩和降维。
# 降维之后特征变成了20维,也就是说特征一共有500行,每行是一个人的特征向量,每个特征向量有20个元素。
# 用随机森林训练模型
pca = decomposition.PCA(n_components=20)
pca.fit(features_train)
features_train = pca.transform(features_train)
features_test = pca.transform(features_test)
regr = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=50, max_depth=None, min_samples_split=10, random_state=0)
regr = regr.fit(features_train, ratings_train)
joblib.dump(regr, './model/face_rating.pkl', compress=1)
# 训练完之后提示训练结束
print('Generate Model Successfully!')
getLandmarks.py
# 人脸关键点提取脚本
import cv2
import dlib
import numpy
# 模型路径
PREDICTOR_PATH = './model/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat'
# 使用dlib自带的frontal_face_detector作为人脸提取器
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
# 使用官方提供的模型构建特征提取器
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor(PREDICTOR_PATH)
face_img = cv2.imread("test_img/test.jpg")
# 使用detector进行人脸检测,rects为返回的结果
rects = detector(face_img, 1)
# 如果检测到人脸
if len(rects) >= 1:
print("{} faces detected".format(len(rects)))
else:
print('No faces detected')
exit()
with open('./results/landmarks.txt', 'w') as f:
f.truncate()
for faces in range(len(rects)):
# 使用predictor进行人脸关键点识别
landmarks = numpy.matrix([[p.x, p.y] for p in predictor(face_img, rects[faces]).parts()])
face_img = face_img.copy()
# 使用enumerate函数遍历序列中的元素以及它们的下标
for idx, point in enumerate(landmarks):
pos = (point[0, 0], point[0, 1])
f.write(str(point[0, 0]))
f.write(',')
f.write(str(point[0, 1]))
f.write(',')
f.write('\n')
f.close()
# 成功后提示
print('Get landmarks successfully')
getFeatures.py
# 特征生成脚本
# 具体原理请参见参考论文
import math
import numpy
import itertools
def facialRatio(points):
x1 = points[0]
y1 = points[1]
x2 = points[2]
y2 = points[3]
x3 = points[4]
y3 = points[5]
x4 = points[6]
y4 = points[7]
dist1 = math.sqrt((x1-x2)**2 + (y1-y2)**2)
dist2 = math.sqrt((x3-x4)**2 + (y3-y4)**2)
ratio = dist1/dist2
return ratio
def generateFeatures(pointIndices1, pointIndices2, pointIndices3, pointIndices4, allLandmarkCoordinates):
size = allLandmarkCoordinates.shape
if len(size) > 1:
allFeatures = numpy.zeros((size[0], len(pointIndices1)))
for x in range(0, size[0]):
landmarkCoordinates = allLandmarkCoordinates[x, :]
ratios = []
for i in range(0, len(pointIndices1)):
x1 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices1[i]-1)]
y1 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices1[i] - 1]
x2 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices2[i]-1)]
y2 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices2[i] - 1]
x3 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices3[i]-1)]
y3 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices3[i] - 1]
x4 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices4[i]-1)]
y4 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices4[i] - 1]
points = [x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4]
ratios.append(facialRatio(points))
allFeatures[x, :] = numpy.asarray(ratios)
else:
allFeatures = numpy.zeros((1, len(pointIndices1)))
landmarkCoordinates = allLandmarkCoordinates
ratios = []
for i in range(0, len(pointIndices1)):
x1 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices1[i]-1)]
y1 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices1[i] - 1]
x2 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices2[i]-1)]
y2 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices2[i] - 1]
x3 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices3[i]-1)]
y3 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices3[i] - 1]
x4 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices4[i]-1)]
y4 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices4[i] - 1]
points = [x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4]
ratios.append(facialRatio(points))
allFeatures[0, :] = numpy.asarray(ratios)
return allFeatures
def generateAllFeatures(allLandmarkCoordinates):
a = [18, 22, 23, 27, 37, 40, 43, 46, 28, 32, 34, 36, 5, 9, 13, 49, 55, 52, 58]
combinations = itertools.combinations(a, 4)
i = 0
pointIndices1 = []
pointIndices2 = []
pointIndices3 = []
pointIndices4 = []
for combination in combinations:
pointIndices1.append(combination[0])
pointIndices2.append(combination[1])
pointIndices3.append(combination[2])
pointIndices4.append(combination[3])
i = i+1
pointIndices1.append(combination[0])
pointIndices2.append(combination[2])
pointIndices3.append(combination[1])
pointIndices4.append(combination[3])
i = i+1
pointIndices1.append(combination[0])
pointIndices2.append(combination[3])
pointIndices3.append(combination[1])
pointIndices4.append(combination[2])
i = i+1
return generateFeatures(pointIndices1, pointIndices2, pointIndices3, pointIndices4, allLandmarkCoordinates)
landmarks = numpy.loadtxt("./results/landmarks.txt", delimiter=',', usecols=range(136))
featuresALL = generateAllFeatures(landmarks)
numpy.savetxt("./results/my_features.txt", featuresALL, delimiter=',', fmt = '%.04f')
print("Generate Feature Successfully!")
Predict.py
# 颜值预测脚本
from sklearn.externals import joblib
import numpy as np
from sklearn import decomposition
pre_model = joblib.load('./model/face_rating.pkl')
features = np.loadtxt('./data/features_ALL.txt', delimiter=',')
my_features = np.loadtxt('./results/my_features.txt', delimiter=',')
pca = decomposition.PCA(n_components=20)
pca.fit(features)
predictions = []
if len(my_features.shape) > 1:
for i in range(len(my_features)):
feature = my_features[i, :]
feature_transfer = pca.transform(feature.reshape(1, -1))
predictions.append(pre_model.predict(feature_transfer))
print('照片中的人颜值得分依次为(满分为5分):')
k = 1
for pre in predictions:
print('第%d个人:' % k, end='')
print(str(pre)+'分')
k += 1
else:
feature = my_features
feature_transfer = pca.transform(feature.reshape(1, -1))
predictions.append(pre_model.predict(feature_transfer))
print('照片中的人颜值得分为(满分为5分):')
k = 1
for pre in predictions:
print(str(pre)+'分')
k += 1
到此这篇关于Python实现对照片中的人脸进行颜值预测的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python对人脸进行颜值预测内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
您可能感兴趣的文章:- OpenCV图像修复cv2.inpaint()的使用
- python 用opencv实现图像修复和图像金字塔
- OpenCV中图像通道操作的深入讲解
- Python深度学习pytorch实现图像分类数据集
- Python实现老照片修复之上色小技巧
 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服