车道线检测是自动驾驶汽车以及一般计算机视觉的关键组件。这个概念用于描述自动驾驶汽车的路径并避免进入另一条车道的风险。
在本文中,我们将构建一个机器学习项目来实时检测车道线。我们将使用 OpenCV 库使用计算机视觉的概念来做到这一点。为了检测车道,我们必须检测车道两侧的白色标记。
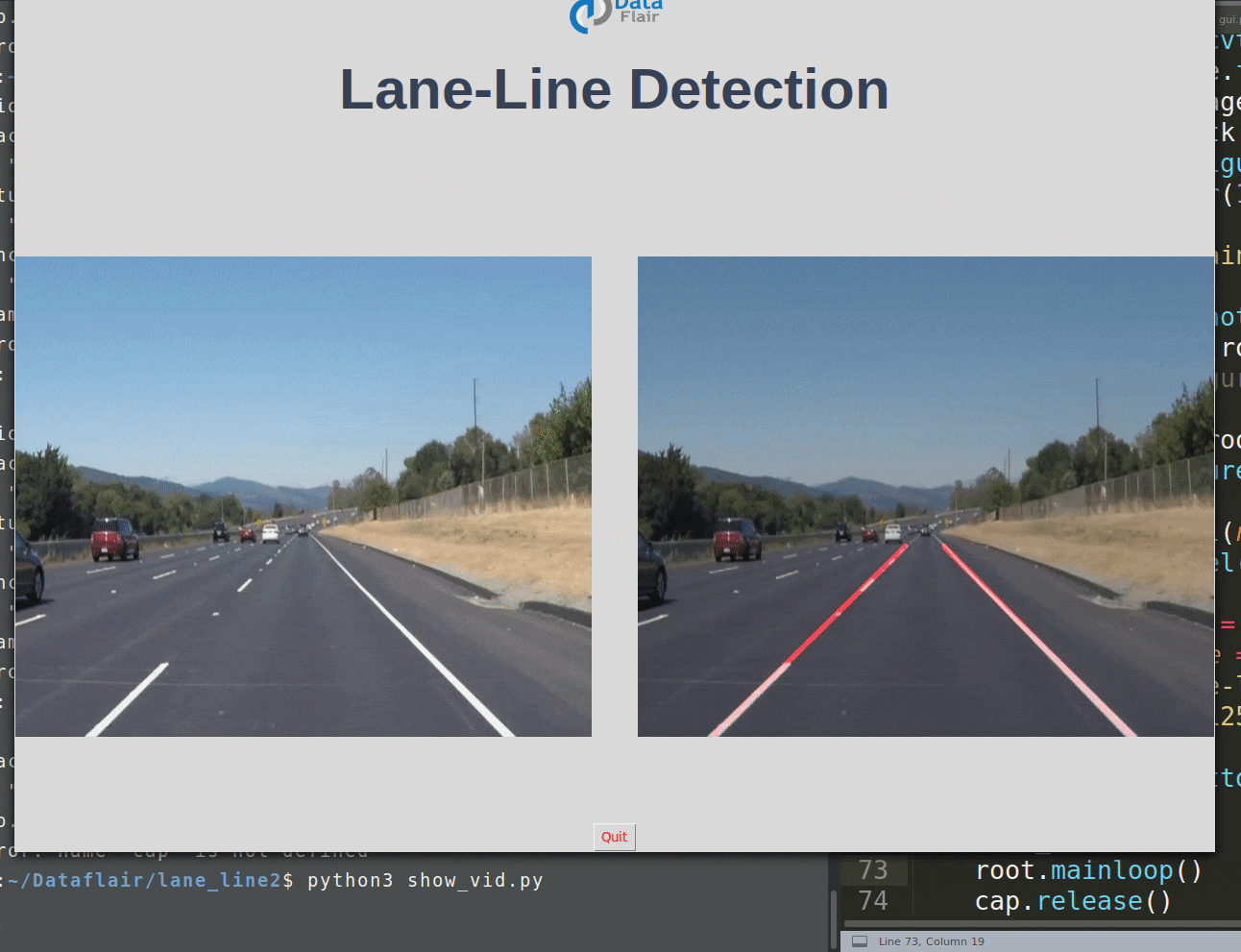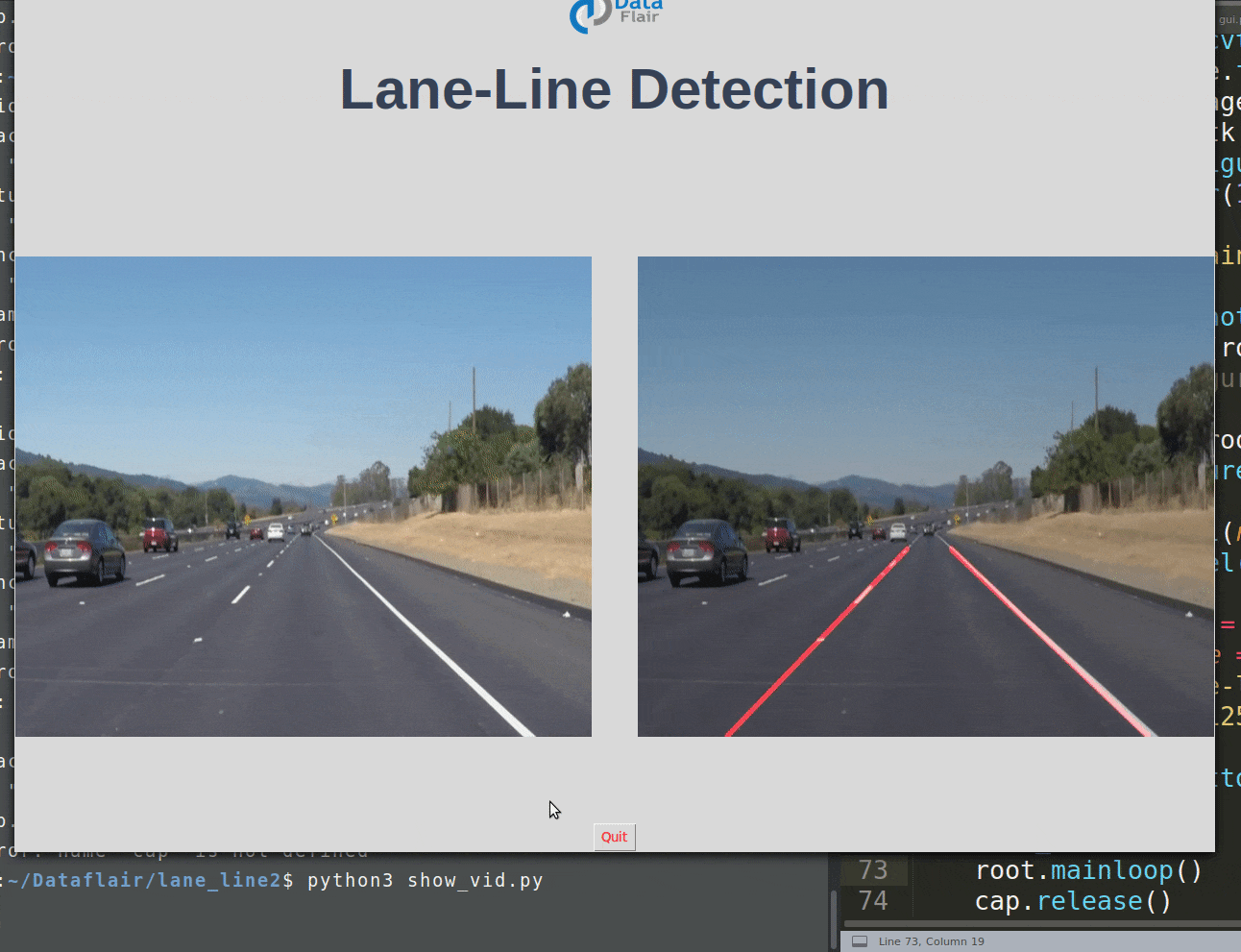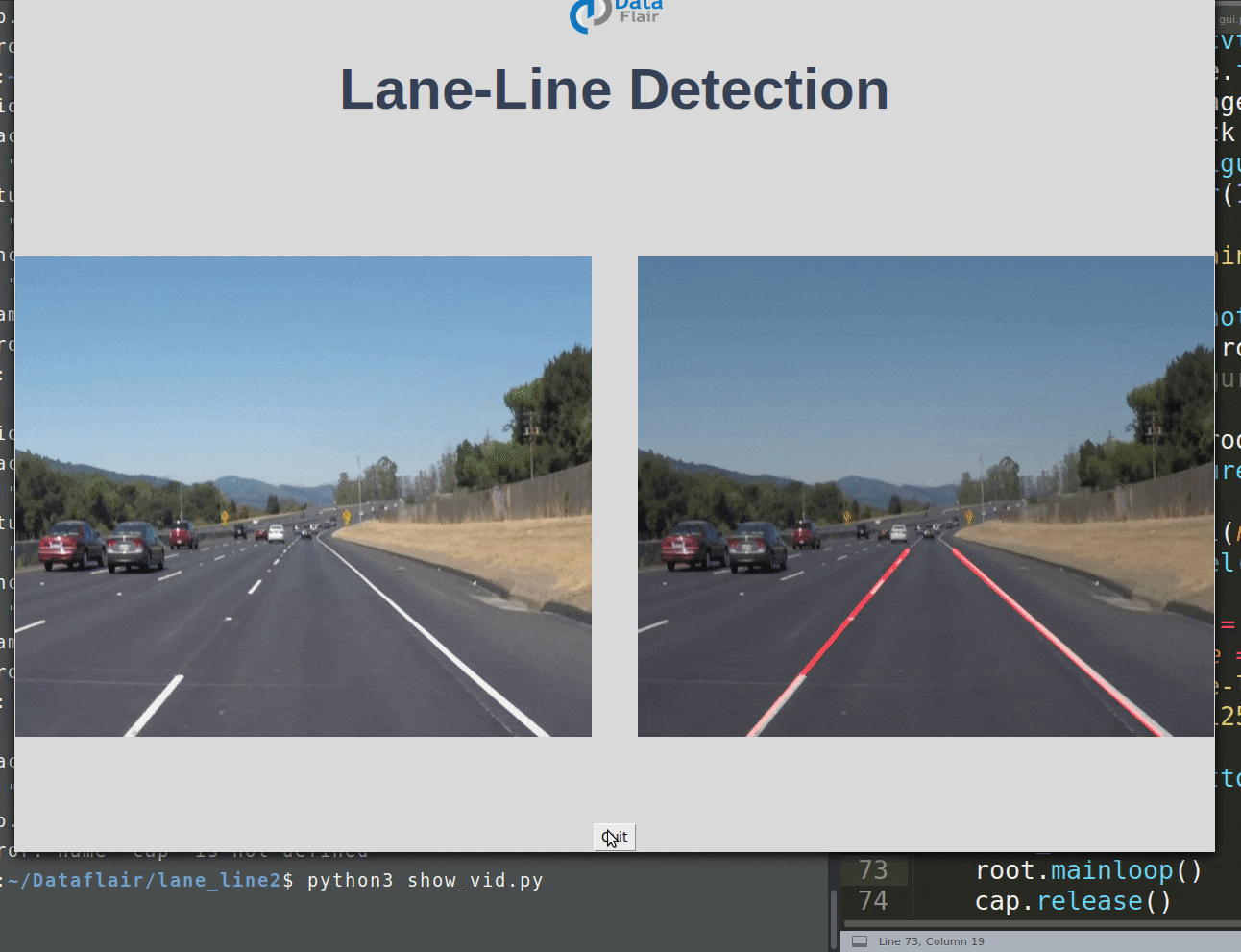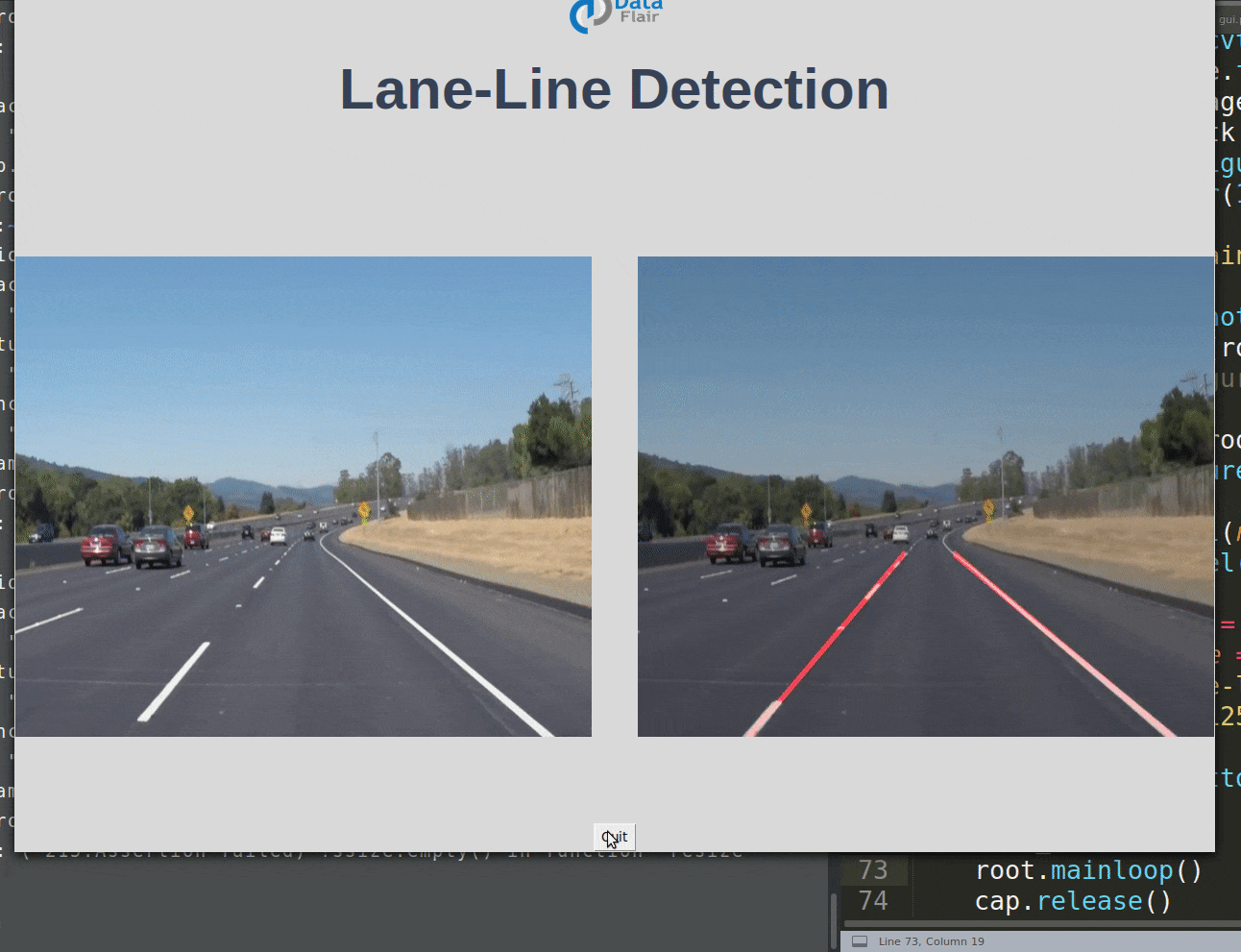
使用 Python 和 OpenCV 进行道路车道线检测
使用 Python 中的计算机视觉技术,我们将识别自动驾驶汽车必须行驶的道路车道线。这将是自动驾驶汽车的关键部分,因为自动驾驶汽车不应该越过它的车道,也不应该进入对面车道以避免事故。
帧掩码和霍夫线变换
要检测车道中的白色标记,首先,我们需要屏蔽帧的其余部分。我们使用帧屏蔽来做到这一点。该帧只不过是图像像素值的 NumPy 数组。为了掩盖帧中不必要的像素,我们只需将 NumPy 数组中的这些像素值更新为 0。
制作后我们需要检测车道线。用于检测此类数学形状的技术称为霍夫变换。霍夫变换可以检测矩形、圆形、三角形和直线等形状。
代码下载
源码请下载:车道线检测项目代码
按照以下步骤在 Python 中进行车道线检测:
1.导入包
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
from moviepy.editor import VideoFileClip
import math
2. 应用帧屏蔽并找到感兴趣的区域:
def interested_region(img, vertices):
if len(img.shape) > 2:
mask_color_ignore = (255,) * img.shape[2]
else:
mask_color_ignore = 255
cv2.fillPoly(np.zeros_like(img), vertices, mask_color_ignore)
return cv2.bitwise_and(img, np.zeros_like(img))
3.霍夫变换空间中像素到线的转换:
def hough_lines(img, rho, theta, threshold, min_line_len, max_line_gap):
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(img, rho, theta, threshold, np.array([]), minLineLength=min_line_len, maxLineGap=max_line_gap)
line_img = np.zeros((img.shape[0], img.shape[1], 3), dtype=np.uint8)
lines_drawn(line_img,lines)
return line_img
4. 霍夫变换后在每一帧中创建两条线:
def lines_drawn(img, lines, color=[255, 0, 0], thickness=6):
global cache
global first_frame
slope_l, slope_r = [],[]
lane_l,lane_r = [],[]
α =0.2
for line in lines:
for x1,y1,x2,y2 in line:
slope = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1)
if slope > 0.4:
slope_r.append(slope)
lane_r.append(line)
elif slope -0.4:
slope_l.append(slope)
lane_l.append(line)
img.shape[0] = min(y1,y2,img.shape[0])
if((len(lane_l) == 0) or (len(lane_r) == 0)):
print ('no lane detected')
return 1
slope_mean_l = np.mean(slope_l,axis =0)
slope_mean_r = np.mean(slope_r,axis =0)
mean_l = np.mean(np.array(lane_l),axis=0)
mean_r = np.mean(np.array(lane_r),axis=0)
if ((slope_mean_r == 0) or (slope_mean_l == 0 )):
print('dividing by zero')
return 1
x1_l = int((img.shape[0] - mean_l[0][1] - (slope_mean_l * mean_l[0][0]))/slope_mean_l)
x2_l = int((img.shape[0] - mean_l[0][1] - (slope_mean_l * mean_l[0][0]))/slope_mean_l)
x1_r = int((img.shape[0] - mean_r[0][1] - (slope_mean_r * mean_r[0][0]))/slope_mean_r)
x2_r = int((img.shape[0] - mean_r[0][1] - (slope_mean_r * mean_r[0][0]))/slope_mean_r)
if x1_l > x1_r:
x1_l = int((x1_l+x1_r)/2)
x1_r = x1_l
y1_l = int((slope_mean_l * x1_l ) + mean_l[0][1] - (slope_mean_l * mean_l[0][0]))
y1_r = int((slope_mean_r * x1_r ) + mean_r[0][1] - (slope_mean_r * mean_r[0][0]))
y2_l = int((slope_mean_l * x2_l ) + mean_l[0][1] - (slope_mean_l * mean_l[0][0]))
y2_r = int((slope_mean_r * x2_r ) + mean_r[0][1] - (slope_mean_r * mean_r[0][0]))
else:
y1_l = img.shape[0]
y2_l = img.shape[0]
y1_r = img.shape[0]
y2_r = img.shape[0]
present_frame = np.array([x1_l,y1_l,x2_l,y2_l,x1_r,y1_r,x2_r,y2_r],dtype ="float32")
if first_frame == 1:
next_frame = present_frame
first_frame = 0
else :
prev_frame = cache
next_frame = (1-α)*prev_frame+α*present_frame
cv2.line(img, (int(next_frame[0]), int(next_frame[1])), (int(next_frame[2]),int(next_frame[3])), color, thickness)
cv2.line(img, (int(next_frame[4]), int(next_frame[5])), (int(next_frame[6]),int(next_frame[7])), color, thickness)
cache = next_frame
5.处理每一帧视频以检测车道:
def weighted_img(img, initial_img, α=0.8, β=1., λ=0.):
return cv2.addWeighted(initial_img, α, img, β, λ)
def process_image(image):
global first_frame
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
lower_yellow = np.array([20, 100, 100], dtype = "uint8")
upper_yellow = np.array([30, 255, 255], dtype="uint8")
mask_yellow = cv2.inRange(img_hsv, lower_yellow, upper_yellow)
mask_white = cv2.inRange(gray_image, 200, 255)
mask_yw = cv2.bitwise_or(mask_white, mask_yellow)
mask_yw_image = cv2.bitwise_and(gray_image, mask_yw)
gauss_gray= cv2.GaussianBlur(mask_yw_image, (5, 5), 0)
canny_edges=cv2.Canny(gauss_gray, 50, 150)
imshape = image.shape
lower_left = [imshape[1]/9,imshape[0]]
lower_right = [imshape[1]-imshape[1]/9,imshape[0]]
top_left = [imshape[1]/2-imshape[1]/8,imshape[0]/2+imshape[0]/10]
top_right = [imshape[1]/2+imshape[1]/8,imshape[0]/2+imshape[0]/10]
vertices = [np.array([lower_left,top_left,top_right,lower_right],dtype=np.int32)]
roi_image = interested_region(canny_edges, vertices)
theta = np.pi/180
line_image = hough_lines(roi_image, 4, theta, 30, 100, 180)
result = weighted_img(line_image, image, α=0.8, β=1., λ=0.)
return result
6. 将输入视频剪辑成帧并得到结果输出视频文件:
first_frame = 1
white_output = '__path_to_output_file__'
clip1 = VideoFileClip("__path_to_input_file__")
white_clip = clip1.fl_image(process_image)
white_clip.write_videofile(white_output, audio=False)
车道线检测项目 GUI 代码:

import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import *
import cv2
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
import os
import numpy as np
global last_frame1
last_frame1 = np.zeros((480, 640, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
global last_frame2
last_frame2 = np.zeros((480, 640, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
global cap1
global cap2
cap1 = cv2.VideoCapture("path_to_input_test_video")
cap2 = cv2.VideoCapture("path_to_resultant_lane_detected_video")
def show_vid():
if not cap1.isOpened():
print("cant open the camera1")
flag1, frame1 = cap1.read()
frame1 = cv2.resize(frame1,(400,500))
if flag1 is None:
print ("Major error!")
elif flag1:
global last_frame1
last_frame1 = frame1.copy()
pic = cv2.cvtColor(last_frame1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = Image.fromarray(pic)
imgtk = ImageTk.PhotoImage(image=img)
lmain.imgtk = imgtk
lmain.configure(image=imgtk)
lmain.after(10, show_vid)
def show_vid2():
if not cap2.isOpened():
print("cant open the camera2")
flag2, frame2 = cap2.read()
frame2 = cv2.resize(frame2,(400,500))
if flag2 is None:
print ("Major error2!")
elif flag2:
global last_frame2
last_frame2 = frame2.copy()
pic2 = cv2.cvtColor(last_frame2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img2 = Image.fromarray(pic2)
img2tk = ImageTk.PhotoImage(image=img2)
lmain2.img2tk = img2tk
lmain2.configure(image=img2tk)
lmain2.after(10, show_vid2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
root=tk.Tk()
lmain = tk.Label(master=root)
lmain2 = tk.Label(master=root)
lmain.pack(side = LEFT)
lmain2.pack(side = RIGHT)
root.title("Lane-line detection")
root.geometry("900x700+100+10")
exitbutton = Button(root, text='Quit',fg="red",command= root.destroy).pack(side = BOTTOM,)
show_vid()
show_vid2()
root.mainloop()
cap.release()
到此这篇关于Python道路车道线检测的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python 道路车道线检测内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服