Python多线程与多进程中join()方法的效果是相同的。
下面仅以多线程为例:
首先需要明确几个概念:
知识点一:
当一个进程启动之后,会默认产生一个主线程,因为线程是程序执行流的最小单元,当设置多线程时,主线程会创建多个子线程,在python中,默认情况下(其实就是setDaemon(False)),主线程执行完自己的任务以后,就退出了,此时子线程会继续执行自己的任务,直到自己的任务结束,
见下面 例子一。
知识点二:
当我们使用setDaemon(True)方法,设置子线程为守护线程时,主线程一旦执行结束,则全部线程全部被终止执行,可能出现的情况就是,子线程的任务还没有完全执行结束,就被迫停止,
见下面例子二。
知识点三:
此时join的作用就凸显出来了,join所完成的工作就是线程同步,即主线程任务在设置join函数的地方,进入阻塞状态,一直等待其他的子线程执行结束之后,主线程再开始执行直到终止终止,
例子见下面三。
知识点四:
join有一个timeout参数:
- 当有设置守护线程时,含义是主线程对于子线程等待timeout的时间将会杀死该子线程,最后退出程序。所以说,如果有10个子线程,全部的等待时间就是每个timeout的累加和。简单的来说,就是给每个子线程一个timeout的时间,让他去执行,时间一到,不管任务有没有完成,直接杀死。
- 没有设置守护线程时,主线程将会等待timeout的累加和这样的一段时间,时间一到,主线程结束,但是并没有杀死子线程,子线程依然可以继续执行,直到子线程全部结束,程序退出。
一:Python多线程的默认情况
import threading
import time
def run():
time.sleep(2)
print('当前线程的名字是: ', threading.current_thread().name)
time.sleep(2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = time.time()
print('这是主线程:', threading.current_thread().name)
thread_list = []
for i in range(5):
t = threading.Thread(target=run)
thread_list.append(t)
for t in thread_list:
t.start()
print('主线程结束!' , threading.current_thread().name)
print('一共用时:', time.time()-start_time)
其执行结果如下:
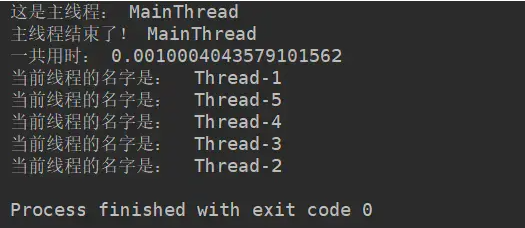
关键:
- 计时是对主线程计时,主线程结束,计时随之结束,打印出主线程的用时。
- 主线程的任务完成之后,主线程随之结束,子线程继续执行自己的任务,直到全部的子线程的任务全部结束,程序结束。
二:设置守护线程
import threading
import time
def run():
time.sleep(2)
print('当前线程的名字是: ', threading.current_thread().name)
time.sleep(2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = time.time()
print('这是主线程:', threading.current_thread().name)
thread_list = []
for i in range(5):
t = threading.Thread(target=run)
thread_list.append(t)
for t in thread_list:
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
print('主线程结束了!' , threading.current_thread().name)
print('一共用时:', time.time()-start_time)
注意:注意请确保setDaemon()在start()之前
其执行结果如下:
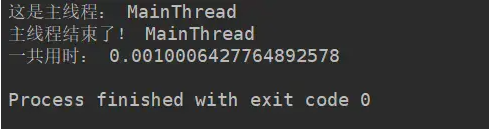
关键点:
非常明显的看到,主线程结束以后,子线程还没有来得及执行,整个程序就退出了。
三:join的作用
import threading
import time
def run():
time.sleep(2)
print('当前线程的名字是: ', threading.current_thread().name)
time.sleep(2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = time.time()
print('这是主线程:', threading.current_thread().name)
thread_list = []
for i in range(5):
t = threading.Thread(target=run)
thread_list.append(t)
for t in thread_list:
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
for t in thread_list:
t.join()
print('主线程结束了!' , threading.current_thread().name)
print('一共用时:', time.time()-start_time)
其执行结果如下:
关键点:
可以看到,主线程一直等待全部的子线程结束之后,主线程自身才结束,程序退出。
主程序意外退出的情况
在线程A中使用B.join()表示线程A在调用join()处被阻塞,且要等待线程B的完成才能继续执行
import threading
import time
def child_thread1():
for i in range(10):
time.sleep(1)
print('child_thread1_running...')
def child_thread2():
for i in range(5):
time.sleep(1)
print('child_thread2_running...')
def parent_thread():
print('parent_thread_running...')
thread1 = threading.Thread(target=child_thread1)
thread2 = threading.Thread(target=child_thread2)
thread1.setDaemon(True)
thread2.setDaemon(True)
thread1.start()
thread2.start()
thread2.join()
1/0
thread1.join()
print('parent_thread_exit...')
if __name__ == "__main__":
parent_thread()
输出:
parent_thread_running...
child_thread1_running...
child_thread2_running...
child_thread1_running...
child_thread2_running...
child_thread1_running...
child_thread2_running...
child_thread1_running...
child_thread2_running...
child_thread1_running...
child_thread2_running...
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "E:/test_thread.py", line 31, in module>
parent_thread()
File "E:/test_thread.py", line 25, in parent_thread
1/0
ZeroDivisionError: integer division or modulo by zero
主线程在执行到thread2.join()时被阻塞,等待thread2结束后才会执行下一句
1/0会使主线程报错退出,且thread1设置了daemon=True,因此主线程意外退出时thread1也会立即结束。thread1.join()没有被主线程执行
总结
到此这篇关于Python多线程以及多线程中join()使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python多线程join()的用法内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
您可能感兴趣的文章:- python 多线程中join()的作用
- python多线程编程中的join函数使用心得
- Python多线程中阻塞(join)与锁(Lock)使用误区解析
- 对python 多线程中的守护线程与join的用法详解
- Python多线程threading join和守护线程setDeamon原理详解
 咨 询 客 服
咨 询 客 服